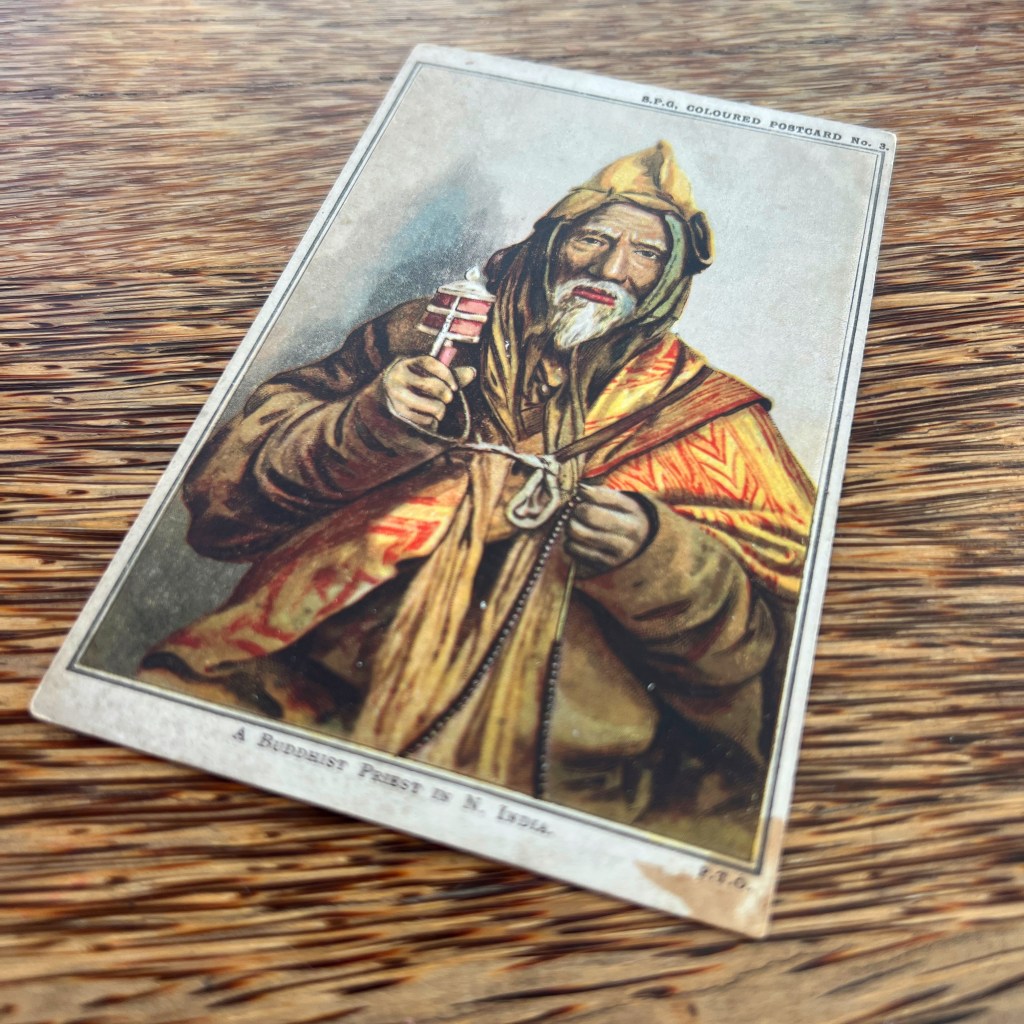
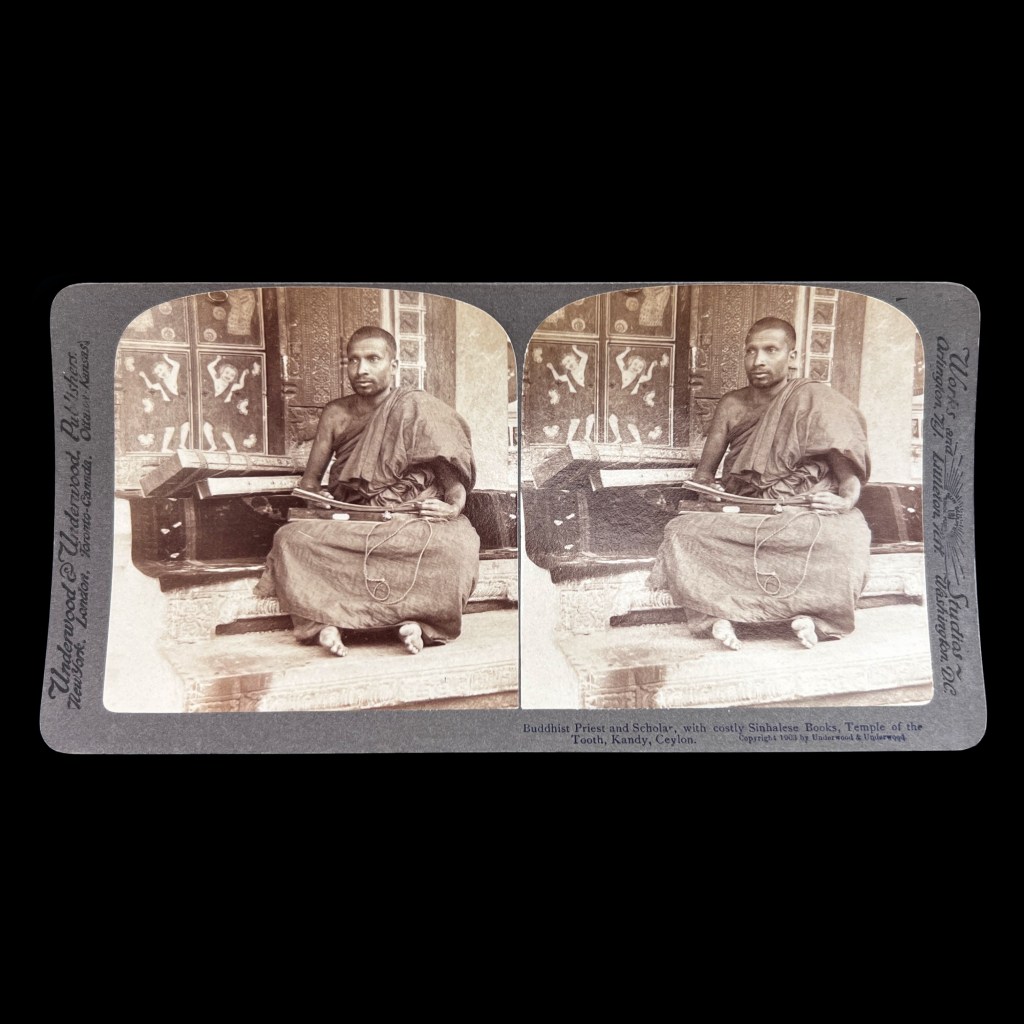
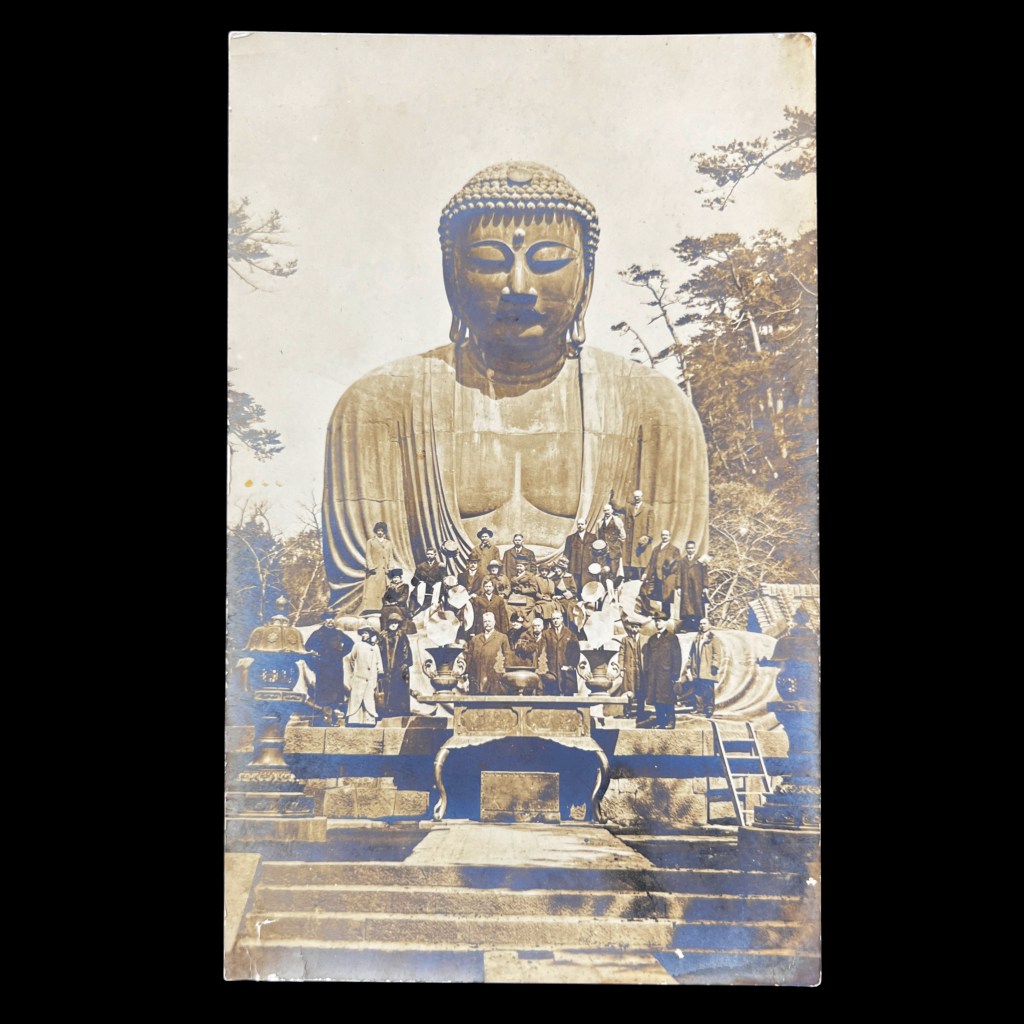
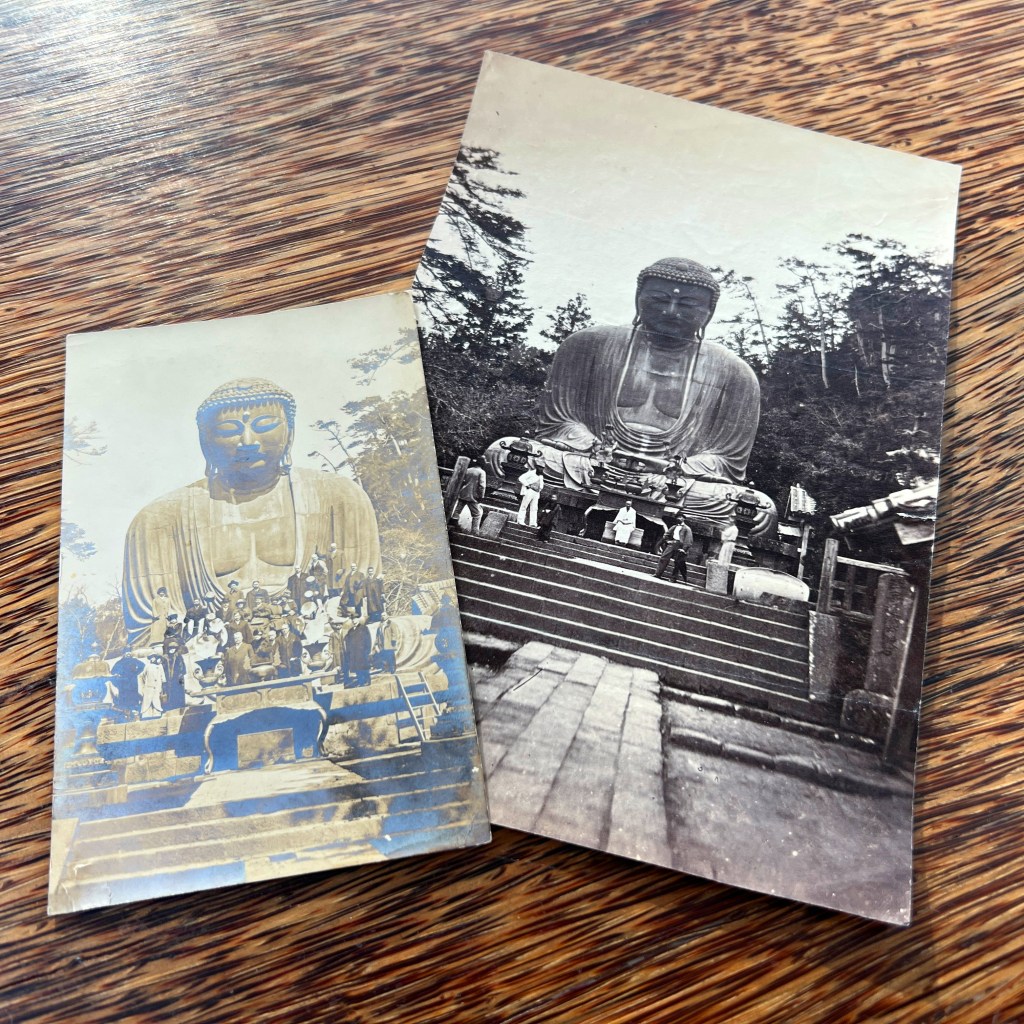
For all the new Buddhas in the West posts
follow us on Bluesky & Instagram
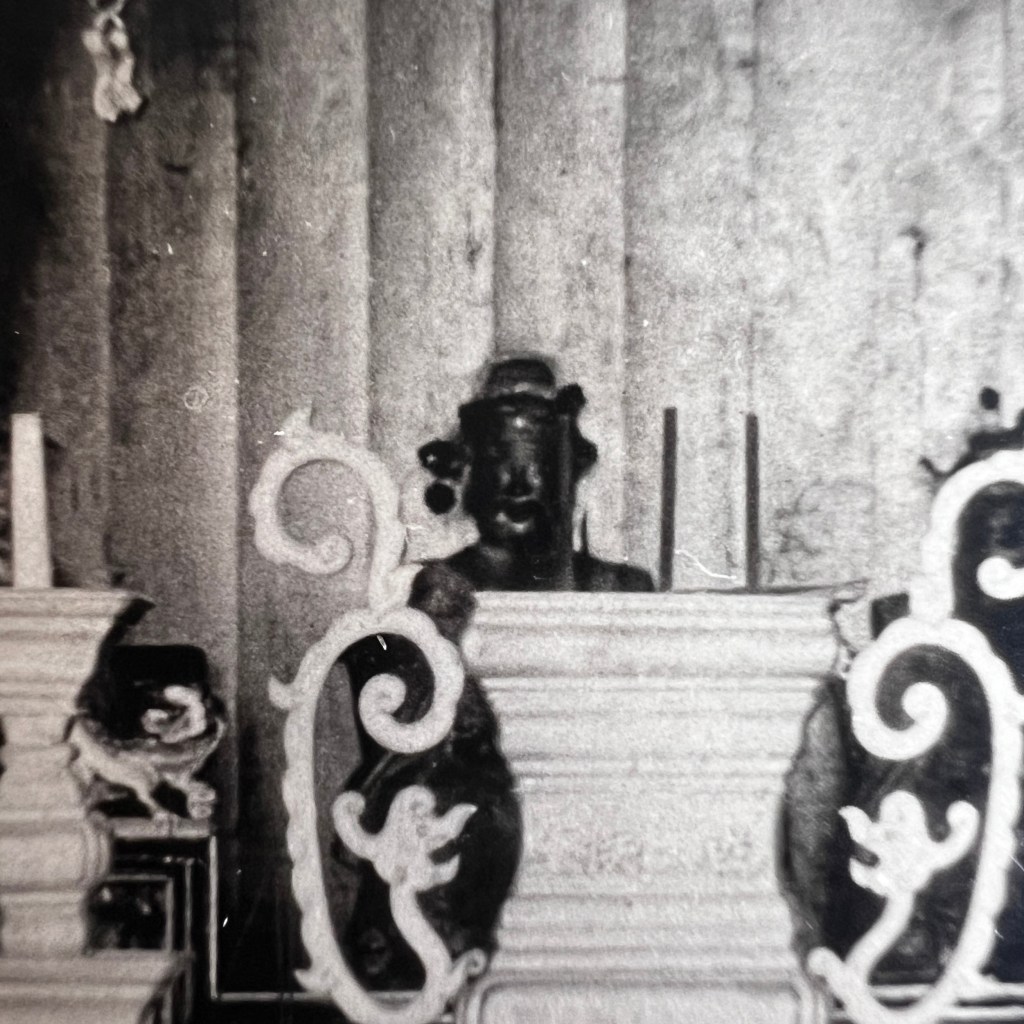
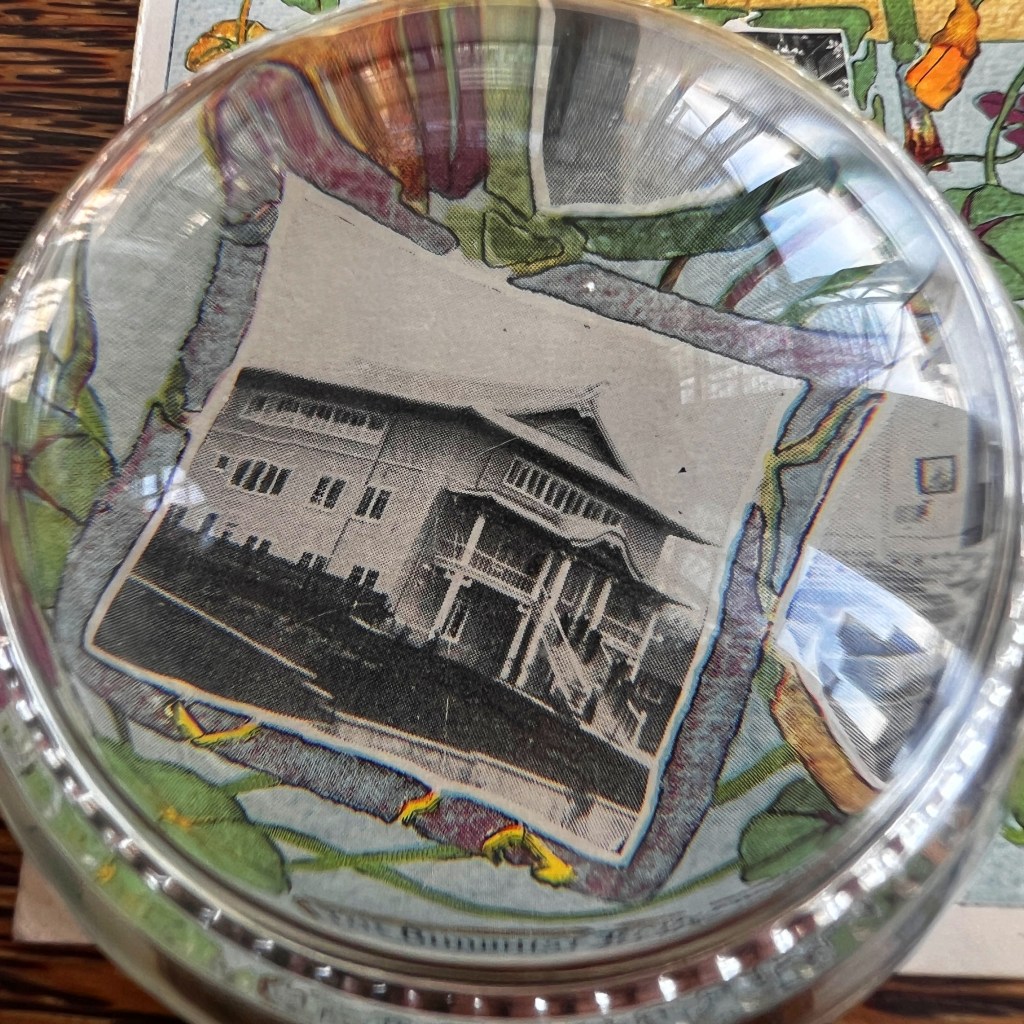
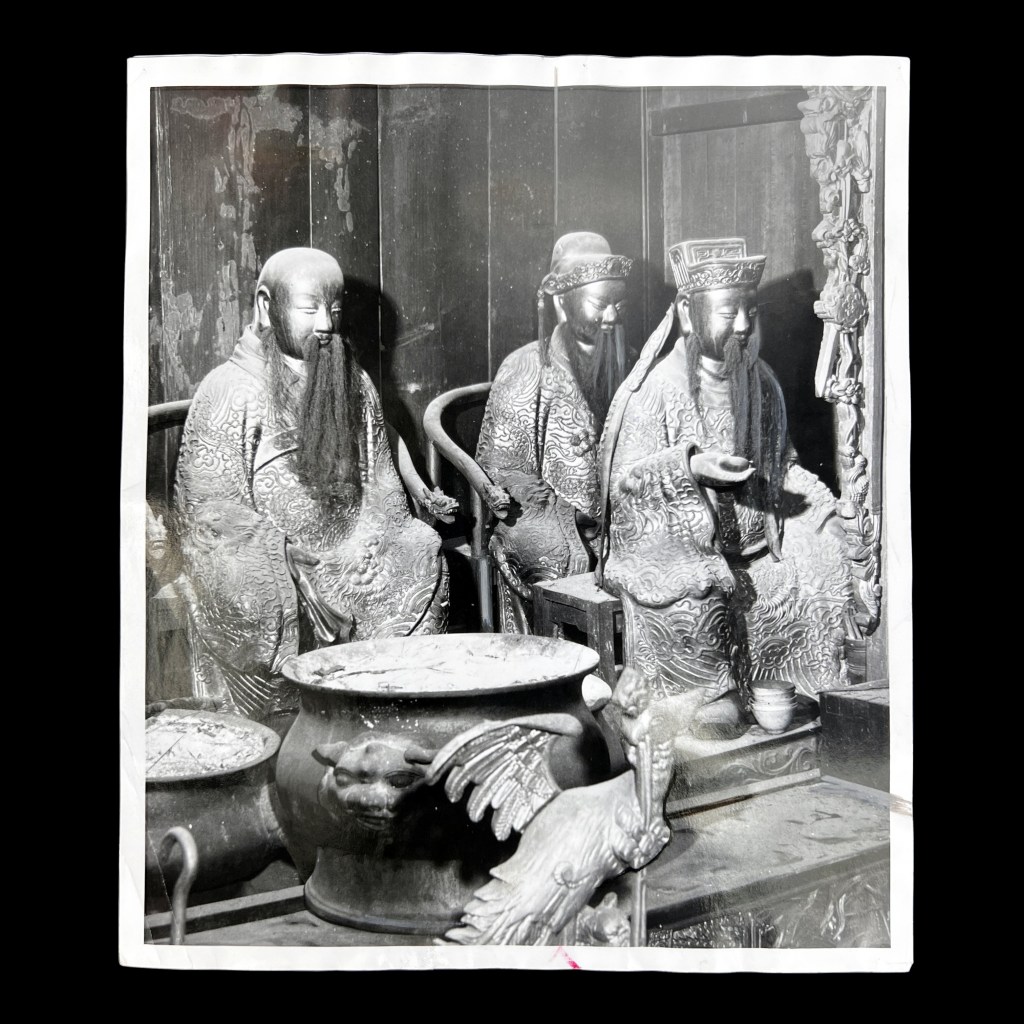
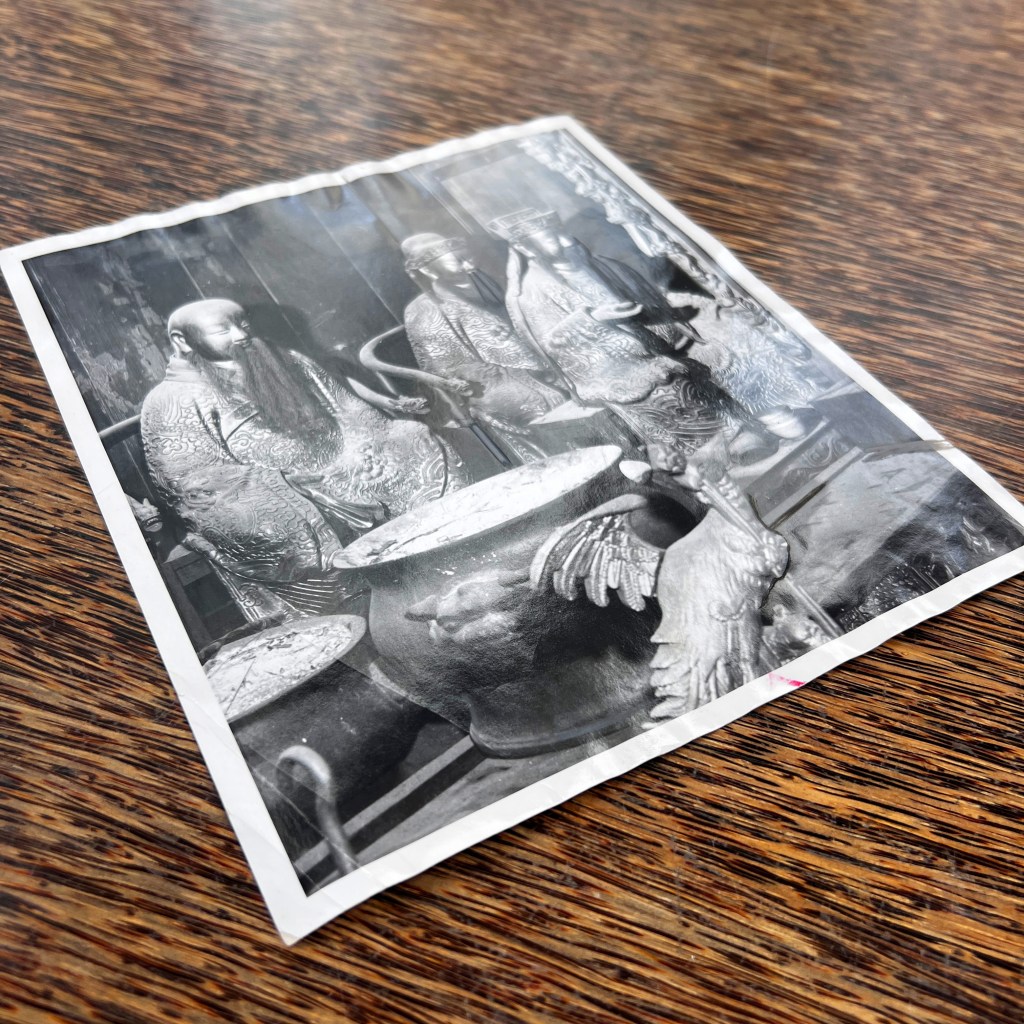
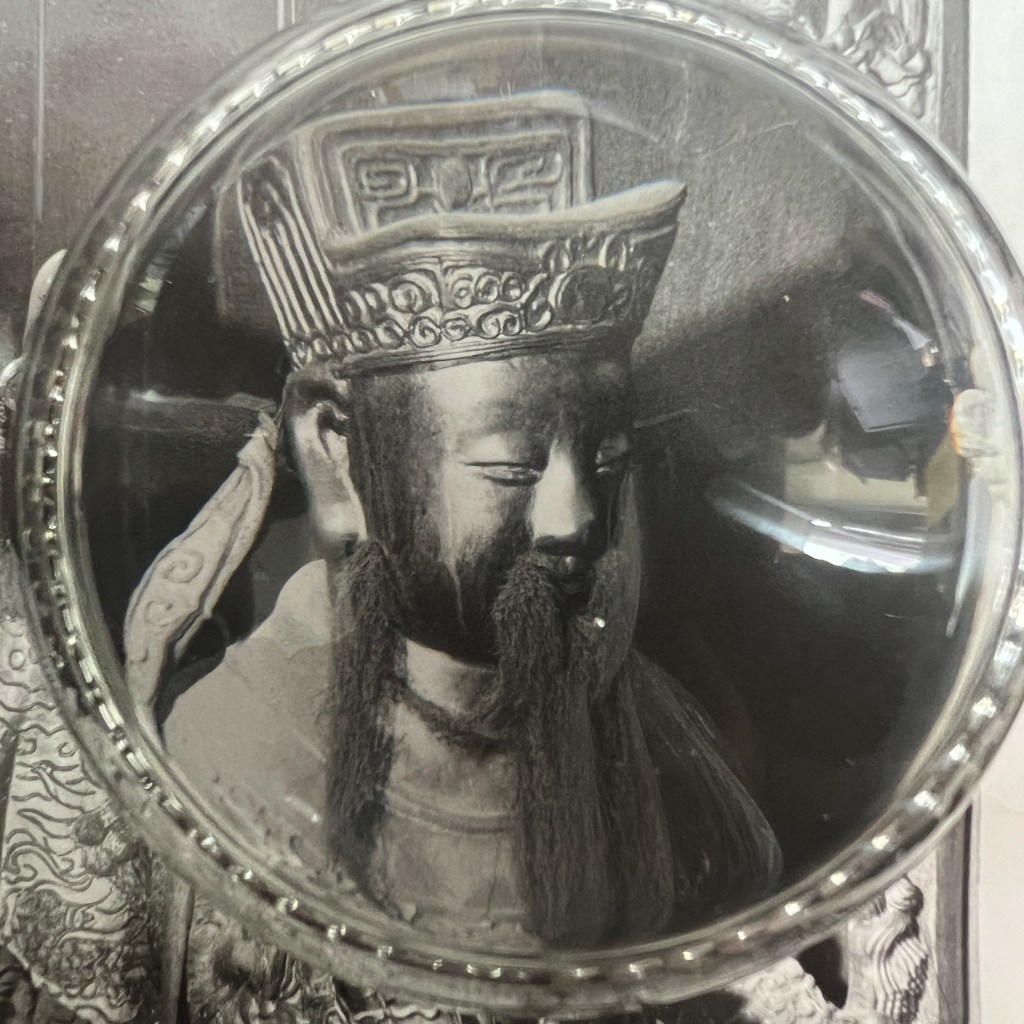
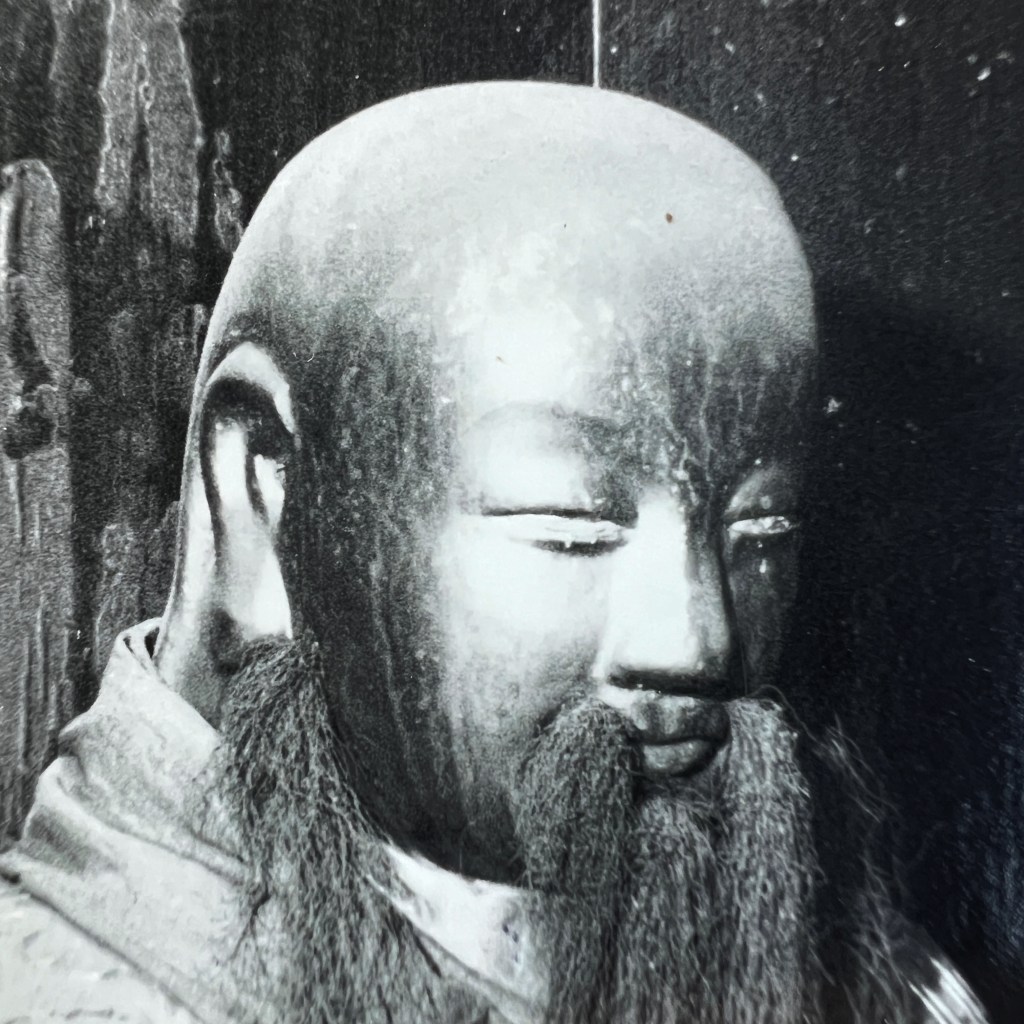
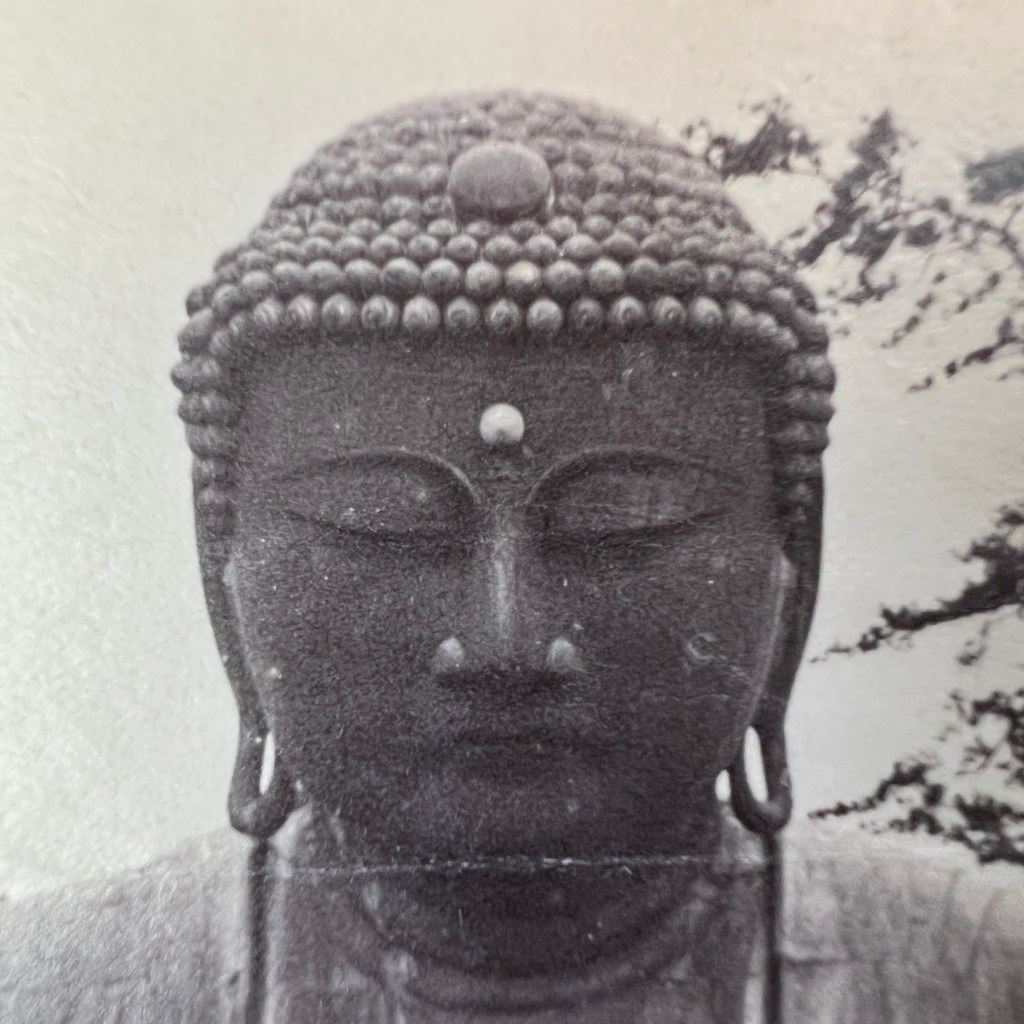
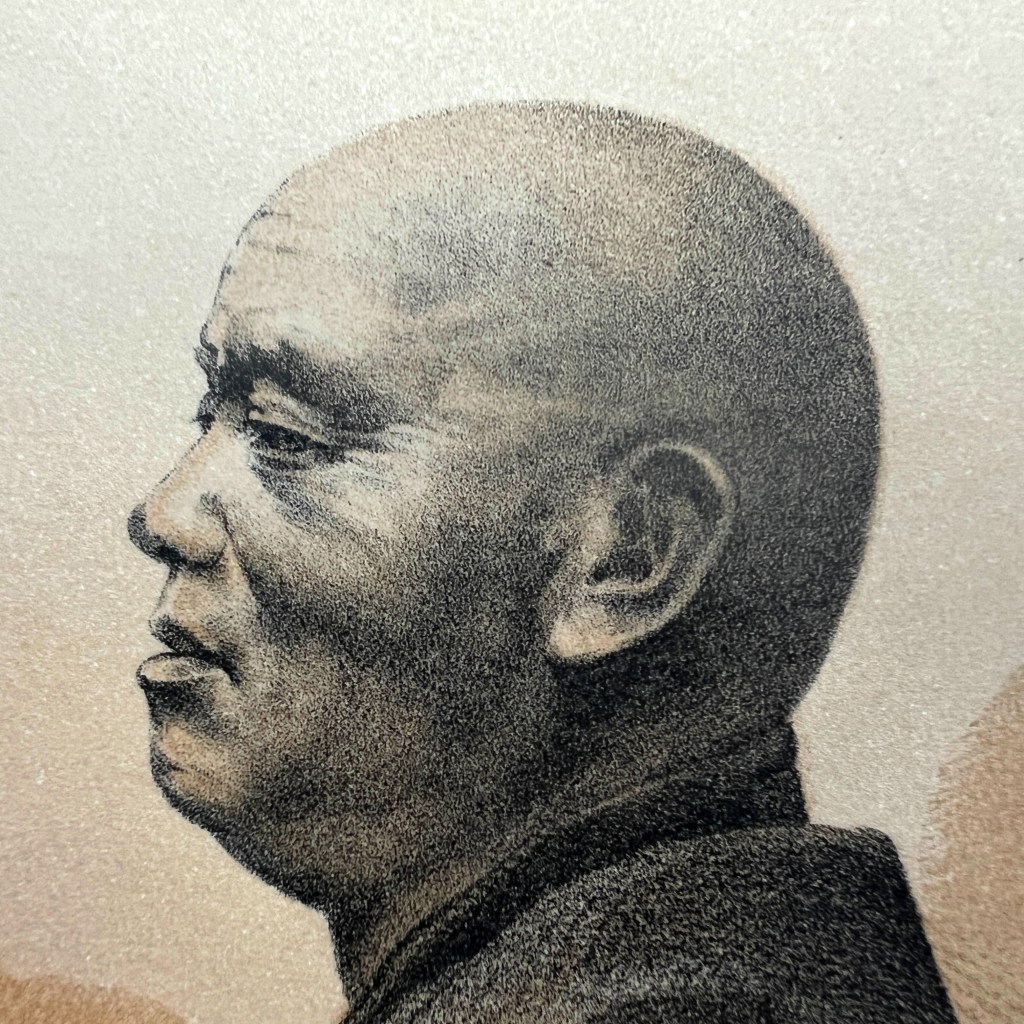
The earliest surviving photographs of Japan were shot by Eliphalet Brown as part of the Perry Expedition in 1853/54. Among many landscapes, Brown also took a few portraits, including this anonymous Buddhist priest at Shimoda – likely the earliest surviving photo of a Buddhist cleric.

Brown reportedly took more than 400 daguerreotypes during the expedition. Several dozen images, including fifteen from Shimoda, were used to illustrate the official US government report published as the Narrative of the Expedition of an American Squadron to the China Seas and Japan in 1856.

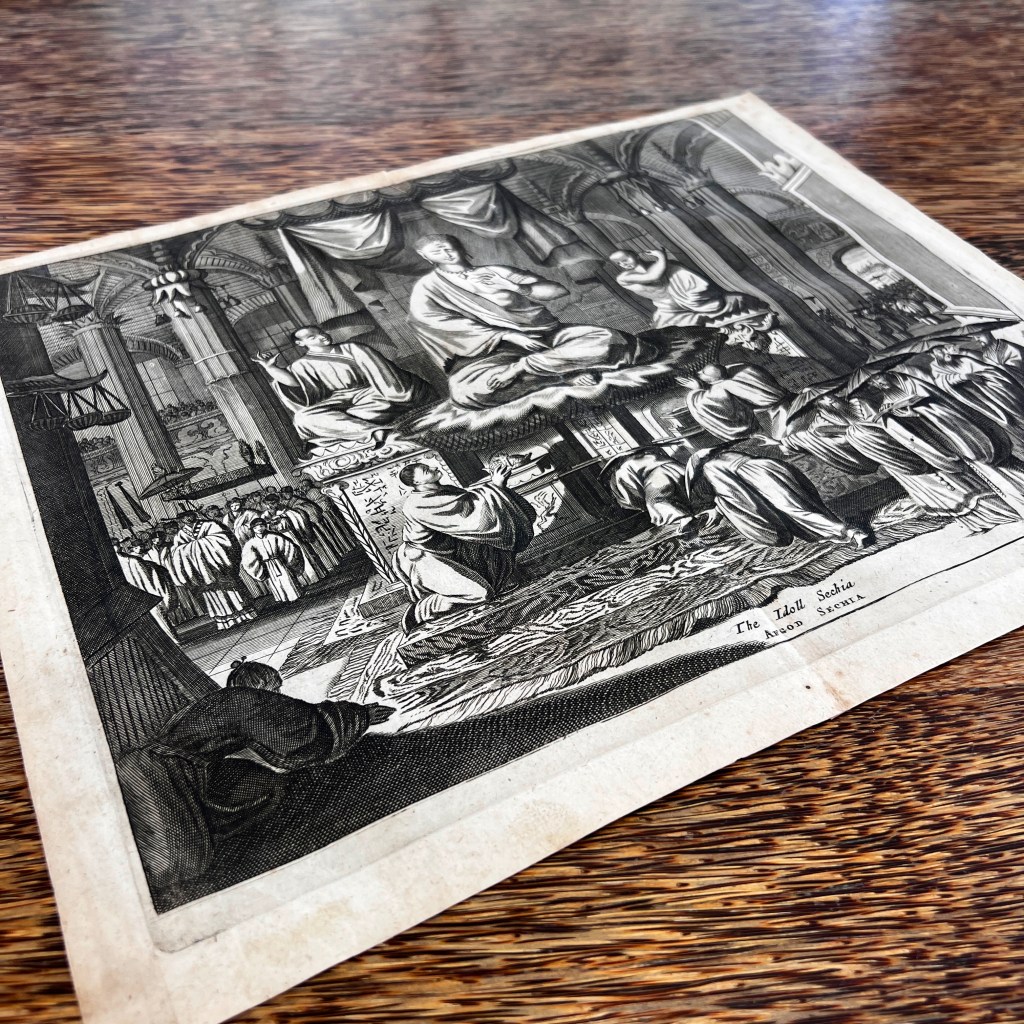
The selected daguerreotypes taken by Brown were first turned into paintings, most often by expedition artist Wilhelm Heine. These were then converted into sepia tone or color-tinted stone lithograph plates for printing; the caption below indicates this image was prepared by artist Peter Krämer.

Lithography is a printing process that uses drawings made with a waxy crayon on a stone plate. Due to a special “gumming” treatment applied to the stone, ink adheres only to the drawn lines, thus allowing prints to be made. The characteristic crayon marks can be easily seen here.

Only six of Brown’s daguerreotypes have been located; some were believed lost when the Philadelphia printer, P. S. Duval, suffered a fire in April 1856. In total, it is believed between 10,000 and 18,000 copies of Perry’s Expedition report were published.

When Perry landed in Shimoda on April 18, 1854, he reported a total of 7,000 inhabitants and nine Buddhist temples. The figure in Brown’s portrait remains unknown. The first volume of Perry’s report is viewable here: https://tinyurl.com/3rpscp9h.


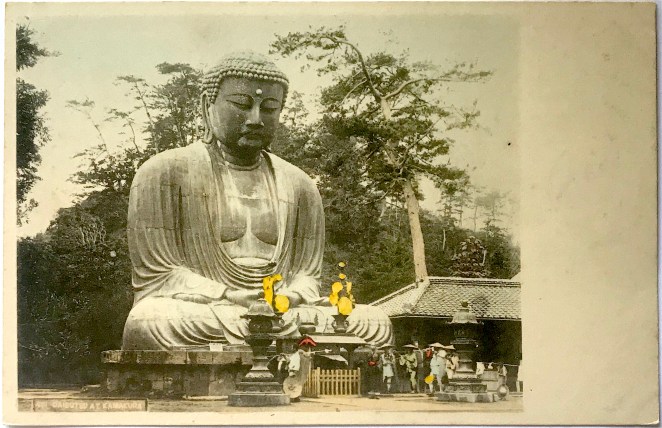
The Buddhas in the West Material Archive is a digital scholarship project that catalogues artifacts depicting Buddhist material culture for Western audiences. It’s comprised of prints, photos, and an assortment of ephemera and other objects. For a brief introduction to this archive, visit the main Buddhas in the West project page.
For Related Buddhas in the West Posts Featuring Buddhist Clerics:
For the Most Recent Buddhas in the West Posts: