The September 1, 1923 Great Kantō Earthquake changed Japan. Striking at just before noon, the 7.9 magnitude earthquake razed the capital of Tokyo and the port of Yokohama and caused severe destruction around the entire Kantō region. The resulting fire and tsunami triggered by the earthquake claimed many more casualties. The resulting reconstruction efforts, involving the rebuilding of homes, government buildings, factories, shops, roads, canals, and bridges was a monumental effort. After seven years of toil, the rebirth of the capital and the symbolic renewal of Japan was marked by a week-long series of celebratory events held in March 1930.
Among the many structures decimated by the disaster also included historic temples and shrines, several of which were in Kamakura, part of what is now considered the Greater Tokyo Area. The ancient capital of Kamakura, after which the Kamakura Period (1185-1333) is named, was the home to the shogunate (bakufu 幕府, “tent government”), a hereditary military dictatorship that ruled over Japan and which granted only nominal authority to the imperial court. While the institution of the shogunate persisted until 1867, the capital was moved at the end of the Kamakura period back to the cultural center of Kyoto. After centuries of gradual decline, significant domestic and international interest was thrust back on to Kamakura in the Meiji period (1868-1912), when its proximity to the newly created international port of Yokohama increased its exposure to travelers and businesses.
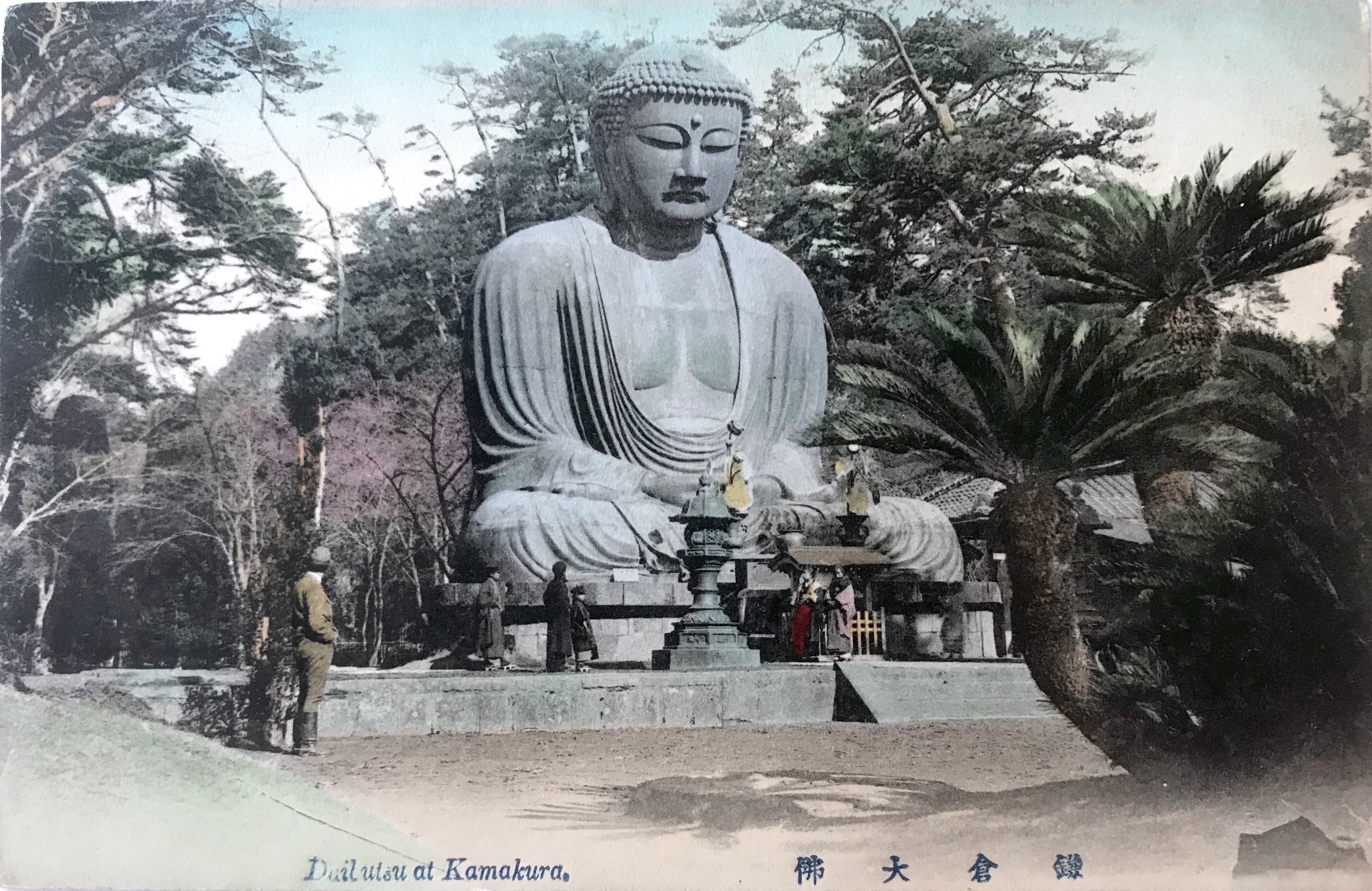
When the 1923 earthquake hit the region, one of the early storylines that spread through American newspapers concerned the survival of the Kamakura Daibutsu, a destination known worldwide among globetrotting tourists. While the 93 metric tonne bronze statue had shifted 30 centimeters forward, warping its back and neck, it survived relatively unharmed. Because of the shift in weight, a portion of the stone pedestal was pushed into the ground. The pedestal itself, however, received extensive structural damage requiring significant repair, which occurred early in 1925.
Sometime after the 1923 earthquake, an unknown publisher issued a set of eight postcards memorializing the scenic views of Kamakura. Thematic sets of postcards had long been manufactured by Japanese publishers, both by private printers and the government. When the government first printed its own picture postcards (ehagaki 絵葉書) in 1902 (private companies were allowed two years earlier), it issued a set of six cards commemorating the Japanese–Korea Treaty of Amity (Nitchō-shūkōjōki 日朝修好条規). Regardless of this precedent for publishing a set of six cards, issuing a set of eight cards soon became standard for postcard publishers.
Why issue a set of eight cards? On theory traces the origin to the artistic preferences of Song Dynasty China. A set of eight scenic vistas has its historical origins in the brush paintings of Chinese artist and government bureaucrat Song Di 宋迪 (c. 1067 – c. 1080) who is attributed with created the visual genre of the Eight Views of the Xiao and Xiang Rivers (Xiāoxiāng Bājǐng瀟湘八景)[Song Di’s paintings are now lost]. The notion that a set of “eight scenic vistas” or “eight views” (hakkei 八景) constituted a complete and integrated set made its way into Japan by the fourteenth-century. This motivated Japanese artisans and poets to find their own groupings of “famous sites” (meisho 名所) and by the Edo period (1615-1868) each province claimed to have its own set of eight special vistas.[1] For example, Kanazawa 金沢 in Sagami Province, in which Kamakura also resides, became among the most famous sets of eight views in Japan, which was visually represented by woodblock artists such as Utagawa Hiroshige 歌川広重 (1797-1858). Perhaps surprisingly, given Kamakura’s historical importance as a national capital, a specific set of eight views was never expressed among pre-Meiji poets, artists, and woodblock printers.[2]
Given the precedence of the literary and artistic value of the eight scenic vistas genre, one could conclude postcard publishers were naturally filling in the gaps of history when they issued sets of eight postcards depicting famous locations around Kamakura. Kanji Satō suggests this would be premature, as it overlooks the particular means of postcard manufacturing. The photomechanical process of printing late Meiji postcards was dominated by the collotype press, which used relatively large sheets of paper that were later cut into individual cards. Each of these sheets accommodated eight individual postcards, thus sets were most efficiently designed in groupings of eight cards, totaling 8, 16, 24, or 32 cards per set. Thus the relationship to the historical groupings of eight scenic vistas portrayed as a “complete” set is most likely coincidental, although it dovetails nicely into traditional Japanese arts.
Figure 1 [Set 1] & Figure 2 [Set 2]
 Sometime in the 1920s sets of picture postcards were more frequently issued in a paper sleeve or cover. These sleeves were initially imprinted with text or simple designs, but due to the highly competitive commercial market these utilitarian items became subject to the same visual expectations as the postcards themselves. The examples before us bear a hand-colored photographic image, which is given the same artistic care as the cards they hold [Fig. 1 & Fig. 2]. In addition to the minor and idiosyncratic coloring differences, each set uses a slightly different letterpress design. Set 2 also appears to be influenced by an Art Deco font style.
Sometime in the 1920s sets of picture postcards were more frequently issued in a paper sleeve or cover. These sleeves were initially imprinted with text or simple designs, but due to the highly competitive commercial market these utilitarian items became subject to the same visual expectations as the postcards themselves. The examples before us bear a hand-colored photographic image, which is given the same artistic care as the cards they hold [Fig. 1 & Fig. 2]. In addition to the minor and idiosyncratic coloring differences, each set uses a slightly different letterpress design. Set 2 also appears to be influenced by an Art Deco font style.
Figure 3 & Figure 4
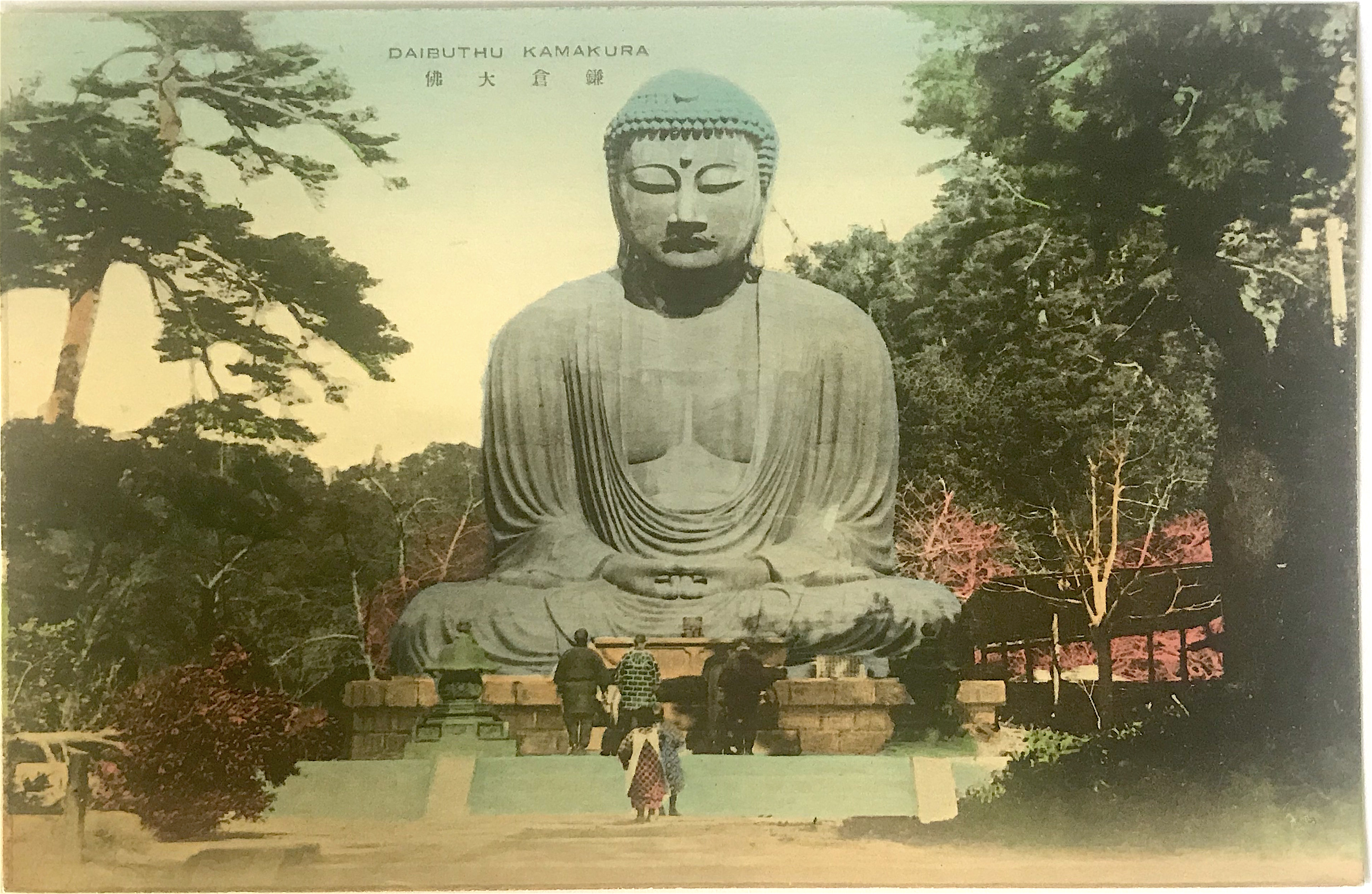


The sleeve image of the Daibutsu matches the photograph of the Daibutsu on the interior postcard, save for the bokashi-style color wash of the sky. Both sleeves show a pink-hued twilight coloring of the sky while the cards are tinted with a daylight blue [Fig. 3 & Fig. 4]. The fact that these selves and cards are hand-colored is partly surprising. In the early part of the twentieth century many monochromatic photographic postcards were hand-tinted. In the early part of the Taishō period (1912-1926), however, a multi-color collotype printing process was developed, presenting a new option for publishers to speed up their production process. Some publishers took advantage of this technology and multi-color printed cards existed side-by-side with hand-tinted cards into the early 1920s. After the 1923 earthquake, however, almost all publishers adopted this new printing technology when they re-opened their businesses. Since these two sets of cards were issued post-1923 (see below), the fact that our unknown publisher was employing hand-coloring was an added selling point – justifiably noted on the sleeve.
Figure 5

Figure 6 [sleeve] & Figure 7 [postcard]


The photograph of the Daibutsu appears staged, as all of the onlookers face squarely towards the colossal statue with legs drawn together and arms at their sides. Upon close inspection, we also see very subtle signs of the 1923 earthquake that ravaged the Kantō region. The lanterns, for example, are shortened from their usual height, signs they needed to be pieced back together and re-erected. Additionally, the items normally arranged atop the offering table are now missing [Figs. 3 &4]. More significantly, the structure to the right of the Daibutsu appears slipshod, a significant difference from the ornate hipped roof building that stood in that same location for three decades [Fig. 5]. Moreover, in a detail that is only visible on the cover sleeves, wooden supports hold up the base of the pedestal, a clear indication of the damages rendered in 1923 [Fig. 6]. An artist carefully painted over the wooden supports for the postcard image, creating a new brick façade to complete the deception [Fig. 7]. The most evident sign of damage is the toppled tree that breaks into the foreground view from the left side [Figs. 3 &4].
Most likely, this photograph represents a period after the terrible destruction caused by the earthquake and after the initial clean-up of the temple grounds. Indeed, enough time has passed so the structure on the right could have been constructed. Yet, the ample work reported in refinishing the pedestal appears to have not yet been executed. Furthermore, in other photographs from April 1925 after the repairs, not only are the wooden supports removed, but the lanterns have been reconstructed fully and moved to the second landing. These details all suggest this photograph of the Daibutsu was taken after the Great Kantō earthquake on September 1, 1923, but before the repairs were finished in early 1925.
Figure 8 [Set 1] & Figure 9 [Set 2]


I suspect that Set 1 was printed in the mid-to-late 1920s. Regrettably, I have not yet been able to match the trademark of a drum (in the stamp box, see Fig. 8) to any known publisher. While Set 2 contains photographs of the same locations, only four of the eight photographs have been copied directly from Set 1. The other four cards offer different vantage points of those locations. Most importantly, the caption (in Japanese only) of the image of the bell tower at Kenchō-ji Temple in Set 2 distinguishes the bell as a National Treasure (kokuhō 國寶)[Fig. 23], a designation it received only on November 14, 1933, thus establishing a firm terminus post quem for this set. I would estimate that Set 2, also issued under an unknown publisher (although I’ve suspected Hoshinoya in the past), was printed in the mid-1930s. I remain uncertain if the same publisher issued both sets.
Below I offer brief historical commentary on the remaining seven views from both sets. The older set, i.e. Set 1, bears simpler captions that are set in blank spaces around the card. The newer set, i.e. Set 2, places the captions along the bottom edge of the cards, as is more traditional. The English in the bilingual caption is sometimes a loose translation of the Japanese, thus I provide a more literal rendering in square brackets.
Figure 10 & Figure 11


- Set 1 caption: Hachiman Temple 鎌倉八幡宮 [Hachiman Shrine, Kamakura]
- Set 2 caption: Hachiman Shrine Kamakura 鎌倉八幡宮 [Hachiman Shrine, Kamakura]
Residing at the geographical center of the city, the unusually long, nearly 2-kilometer long road leading to the Hachiman Shrine entrance traditionally doubled as the main thoroughfare of the city. Originally constructed in 1063, the founder of the Kamakura shogunate, Minamoto no Yoritomo 源頼朝 (1147-99), invited the tutelary kami of warriors, Hachiman 八幡, to reside in a new reconstruction of the shine in order to protect his fledgling government. Due to its relationship with the shogun and important political role, the Hachiman Shrine remains the most historically and culturally important site in Kamakura. Previous to 1868, this site was a shrine-temple complex (jingū-ji 神宮寺), meaning it was used as a place for Buddhist practice and the worship of kami.
Figure 12 & Figure 13
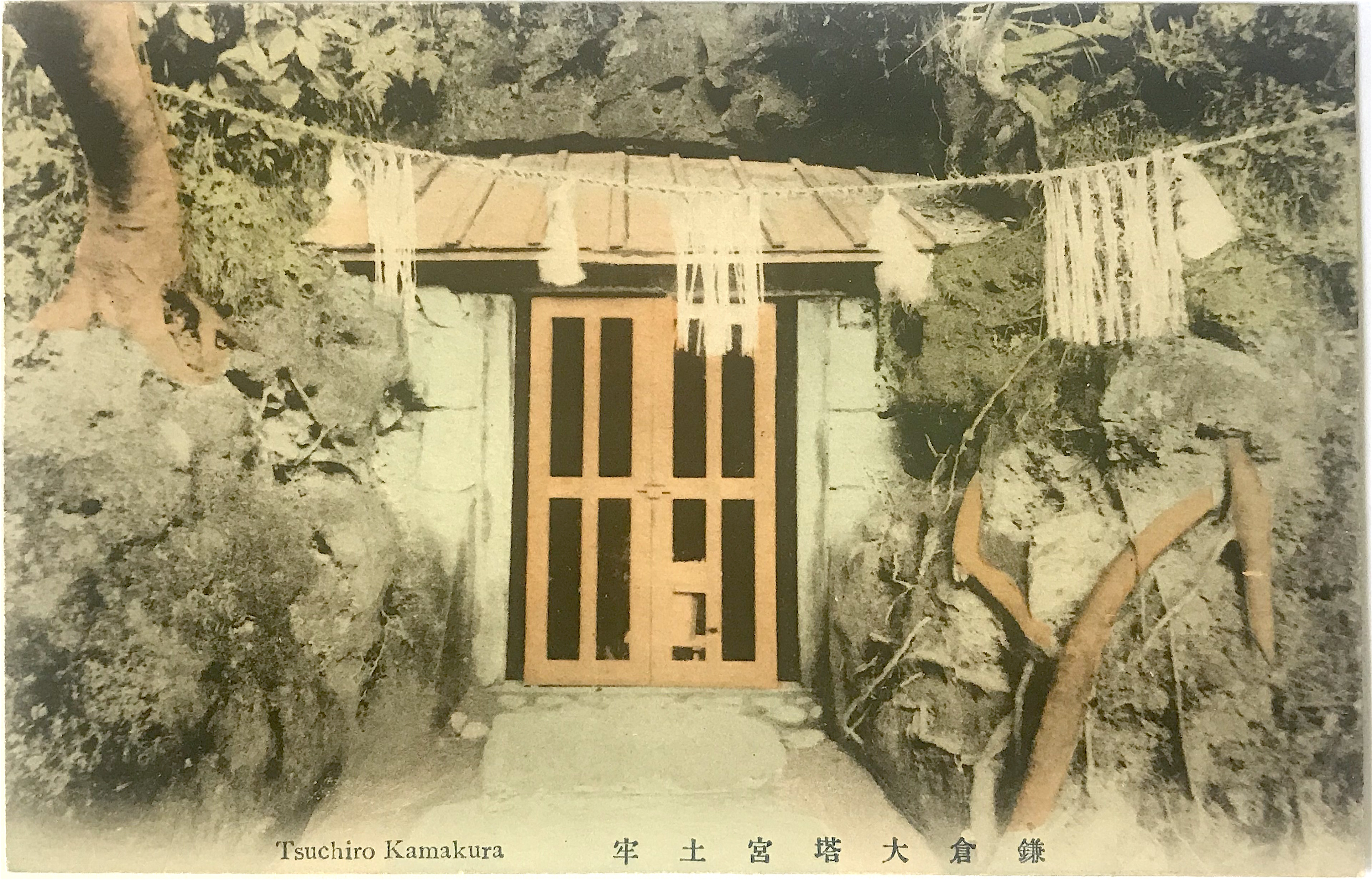


- Set 1 caption: Tsuchiro Kamakura 鎌倉大塔宮土牢 [“The prison at Ōtōnomiya Shrine, Kamakura”]
- Set 2 caption: Tsuchiro Kamakura 鎌倉大塔宮土牢 [“The prison at Ōtōnomiya Shrine, Kamakura”]
The Kamakura Shrine was erected by Emperor Meiji in 1869 to honor Prince Moriyoshi 護良親王 (also read Morinaga) (1308-1335) who was imprisoned and killed as an act of political retribution in 1335. Before he actively helped his father lead forces against the shogun, Moriyoshi was a Buddhist monk and previously held the position of head abbot of Enryaku-ji Temple 延暦寺, the prestigious seat of the Tendai school.[3] Moriyoshi’s life and unfortunate death captured the imagination of the Japanese and he was well known even before the creation of the shrine memorializing him. The postcard photograph depicts the cave behind the main shrine hall (haiden 拝殿), which according to tradition is where the prince was held captive for nine months. The alternate name of this site is Ōtōnomiya Shrine 大塔宮, for a pseudonym used by Moriyoshi.
Figure 14 & Figure 15


Set 1 caption: View of Yenoshima 七里ヶ濱ヨリ江ノ島ヲ望 [Distant View of Enoshima from Shichirigahama]
Set 2 caption: View of Enoshima (Island) near Kamakura 七里ヶ濱ヨリ江ノ島ヲ望ム [Distant View of Enoshima from Shichirigahama]
Figure 16 & Figure 17


- Set 1: View of Yenoshima 江ノ島入口 [The Entrance to Enoshina]
- Set 2: Entrance of Enoshima (Island) near Kamakura 江ノ島入口棧橋 [The Entrance Bridge to Enoshina]
The famed island of Enoshima is a center of worship to the goddess Benzaiten 弁財天, a figure with origins in India and who entered Japan in the 6th through 8th centuries. As one of her roles, Benzaiten was considered the protector of the nation and thus was favored by military leaders. The founder of the Kamakura shogunate, Minamoto no Yoritomo 源頼朝 (1147-99), took advantage of the proximity of Enoshima to his new capital and mandated the construction of a torii on the island to memorialize his devotion to the goddess. Taking advantage of visitors to the islands, entrepreneurs soon set up a variety of shops, consequently making the excursion even more attractive to travelers. For early Western tourists, the sandy beaches made the island a favorite resort area. Older woodblock prints show that the island was connected to the Shichirigahama beach by a shallow sandbar before the bridge was constructed.
Figure 18 & Figure 19


- Set 1 caption: Hase Temple 鎌倉長谷寺 [Hasa-dera Temple, Kamakura]
- Set 2 caption: Hase Temple Kamakura 鎌倉長谷寺 [Hasa-dera Temple, Kamakura]
With origins in the 8th century, this temple is best known for housing one of the largest wooden statues in Japan. It is a 9 meter (approx. 30 foot) tall statue of the Buddhist goddess Kannon 觀音. Its purported origins are rather interesting. It is believed an artist named Tokudo 徳道 made two large Kannon statues from a single fragrant camphor tree in 721. One was enshrined in Hase-dera Temple in Nara, while the second was set adrift into the sea. Fifteen years later the wooden statue washed ashore near Kamakura and a temple, also named Hase-dera, was constructed to honor it. Like many religious sites in Kamakura during the Kamakura period, this temple was restored and expanded. Several later postcard sets of Kamakura include a view of the Kannon statue.
Figure 20 & Figure 21
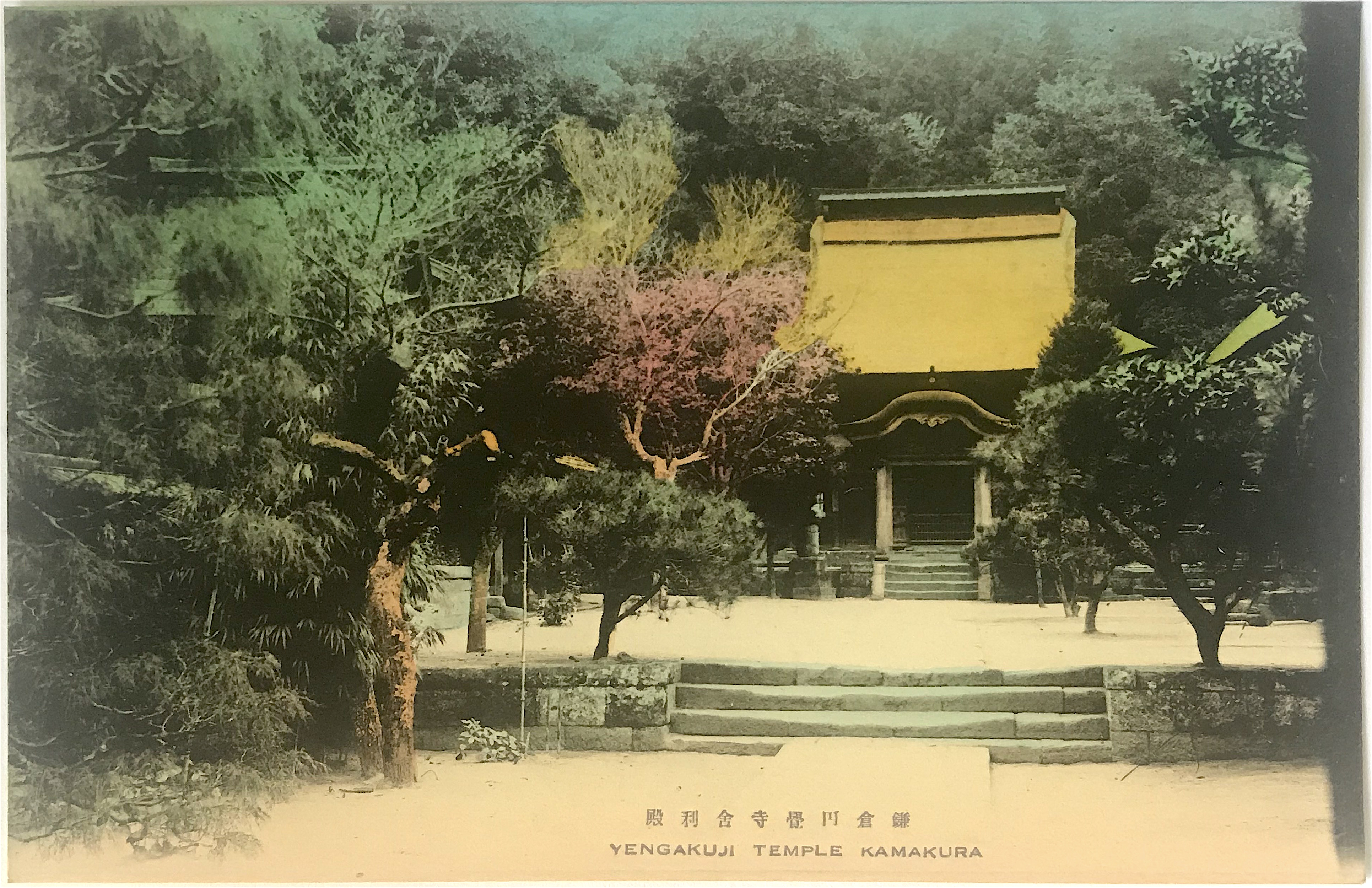
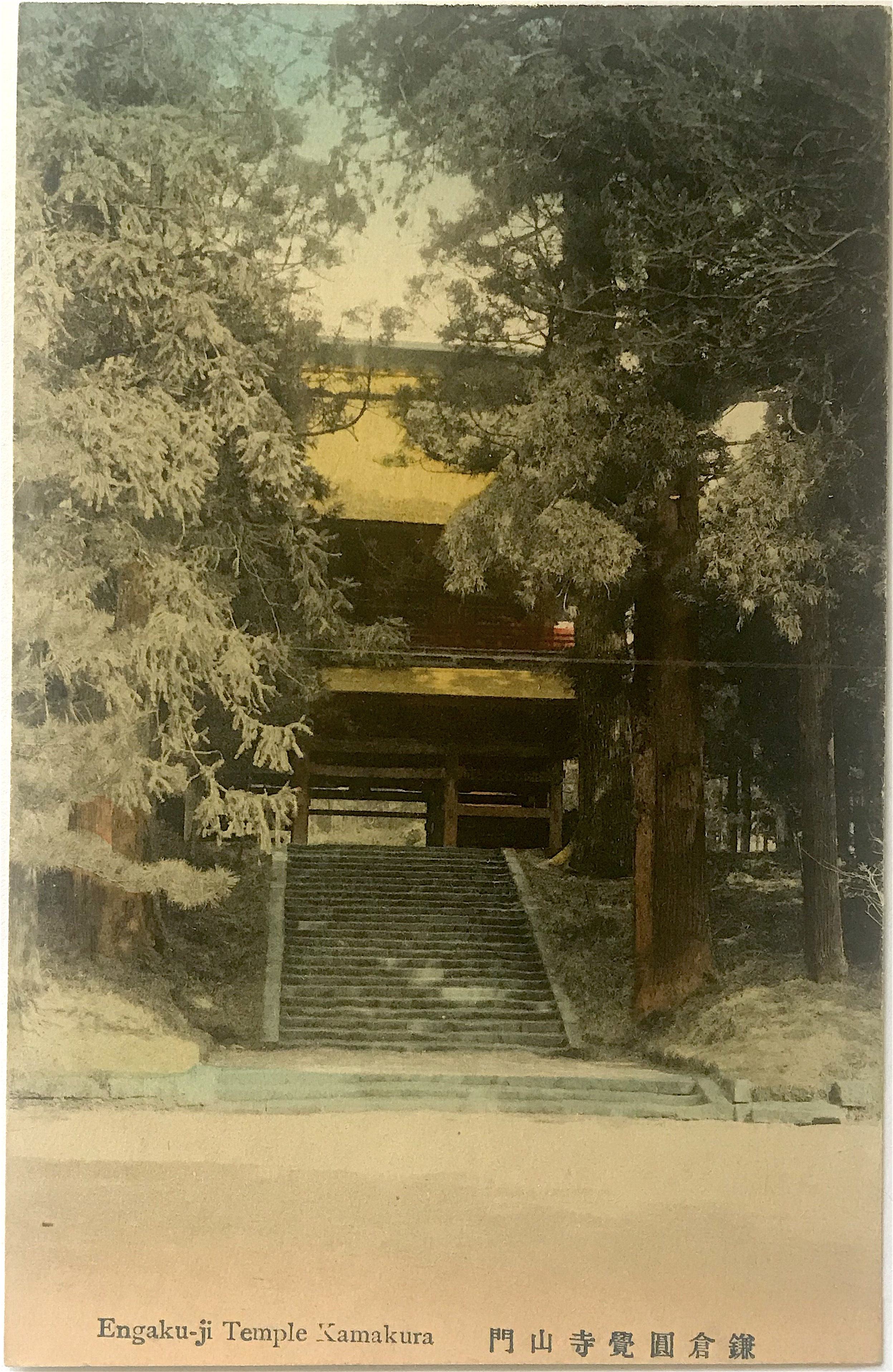


- Set 1: Yengakuji Temple Kamakura 鎌倉円覚寺舍利殿 [Reliquary Hall of Engaku-ji Temple, Kamakura]
- Set 2: Engaku-ji Temple Kamakura 鎌倉圓覺寺山門 [Front Entrance of Engaku-ji Temple, Kamakura]
Founded in 1282 during the Kamakura period, Engaku-ji Temple was included as one of the Kamakura’s “Five Mountains” (gozan 五山), a network of Zen Buddhist temples supervised by a state bureaucracy but that also received the state’s protection. In the Meiji period (1868-1912) it became the center for Zen study in the eastern part of Japan. Not coincidentally, the famed popularizer of Zen in America, D.T. Suzuki (1870-1966), trained there (though he remained a layperson until his death). Set 1 depicts the temple Reliquary Hall (noted in the Japanese caption) which houses a tooth of the Buddha. This building is registered as a National Treasure. Set 2 depicts the temple front gate (sanmon 山門, “mountain gate”), itself a prominent piece of architecture on the temple grounds.
Figure 22 & Figure 23
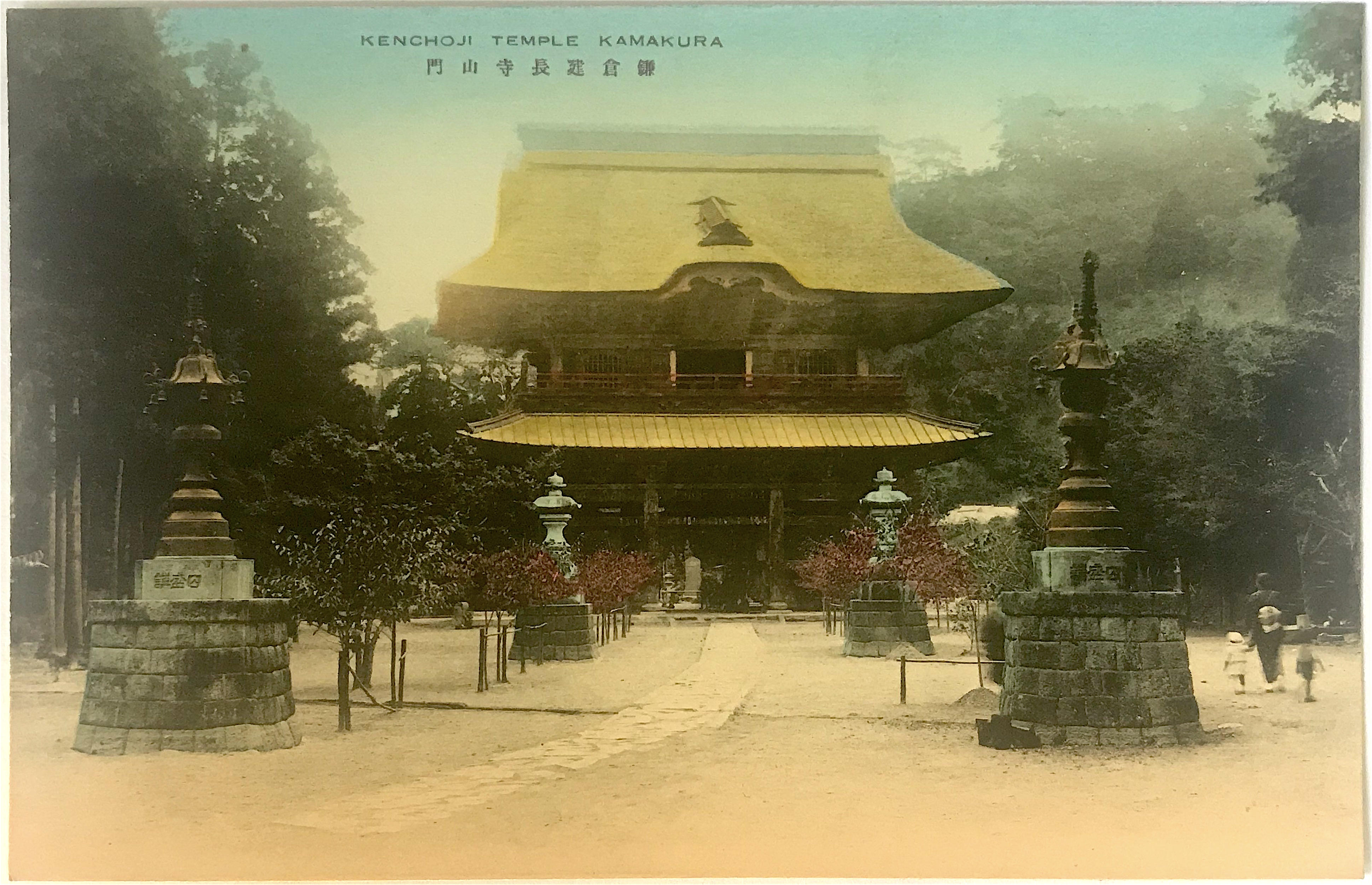


- Set 1 caption: Kenchoji Temple Kamakura 鎌倉建長寺山門 [Front Entrance of Kenchō-ji Temple, Kamakura]
- Set 2 caption: Tsurigane (Bell-Tower) Kencho-ji Temple Kamakura 鎌倉建長寺鐘樓(國寶) [Bell Tower at Kenchō-ji Temple, Kamakura (National Treasure)]
Founded in 1253 during the Kamakura period, Kenchō-ji is the oldest Zen training temple in Japan. Like Engaku-ji, it was also included among the “Five Mountains” network. Set 1 depicts the temple front gate. And while Set 2 depicts the bell tower, the significant historical entity is the temple bell (bonshō 梵鐘), itself designated as a National Treasure (kokuhō 國寶), the most precious of Japan’s historic and cultural properties. Cast in 1255 by Mononobe Shigemitsu 物部重光 it is the second largest in the Kantō region, only to one housed in Engaku-ji. It is believed that the goddess Benzaiten, who was thought to reside on the nearby island of Enoshima (see above), offered her divine protection to have it made. Some modern scholars have suggested Mononobe as the caster of the Kamakura Daibutsu since this bell was made around the same period, although this remains unlikely.
Notes:
*This is part of a series of posts devoted to exploring the development of a visual literacy for Buddhist imagery in America. All items (except otherwise noted) are part of my personal collection of Buddhist-themed ephemera. I have also published my working notes on identifying publishers of Meiji and early Taishō postcards and establishing a sequential chronology for Kamakura Daibutsu photographs.
[1] Shirane 2010.
[2] Nenzi (2004) outlines the development of Kamakura and Sagami generally into a destination spot through the identification of “tourist packages.”
[3] Moriyoshi (his Buddhist name was Son’un 尊雲) had a complex relationship to his monastic vocation, since his vital role as abbot was to enlist the help of important temples and warrior monks to help his father, Emperor Go-Daigo 後醍醐天皇 (1288-1339), in his fight against the Kamakura shogunate.




 The photograph of the Daibutsu by Esaki (or one of his studio assistants) depicts the bronze statue from the southwest corner, an uncommon, but
The photograph of the Daibutsu by Esaki (or one of his studio assistants) depicts the bronze statue from the southwest corner, an uncommon, but 
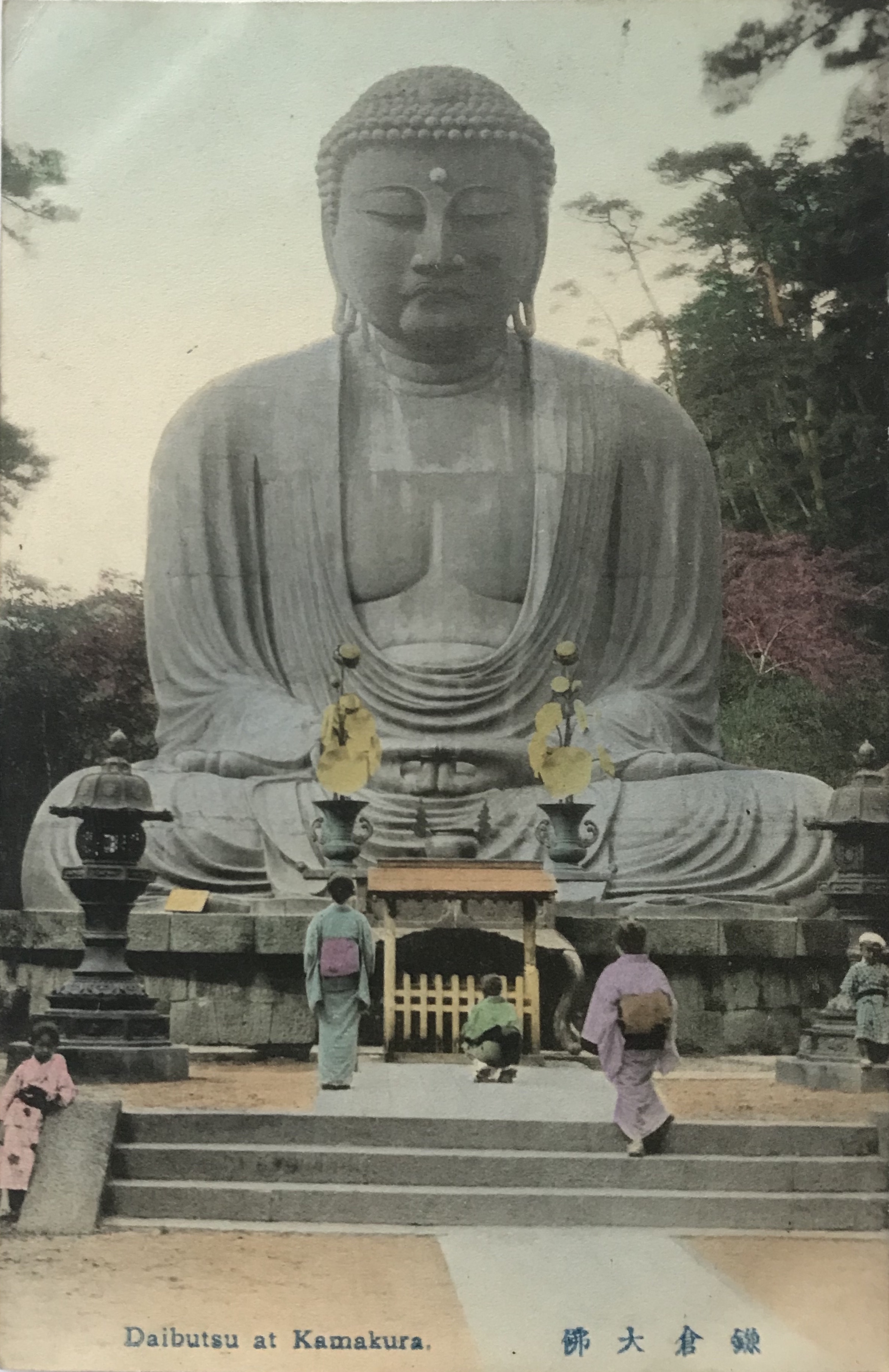











 The full postcard can be found
The full postcard can be found