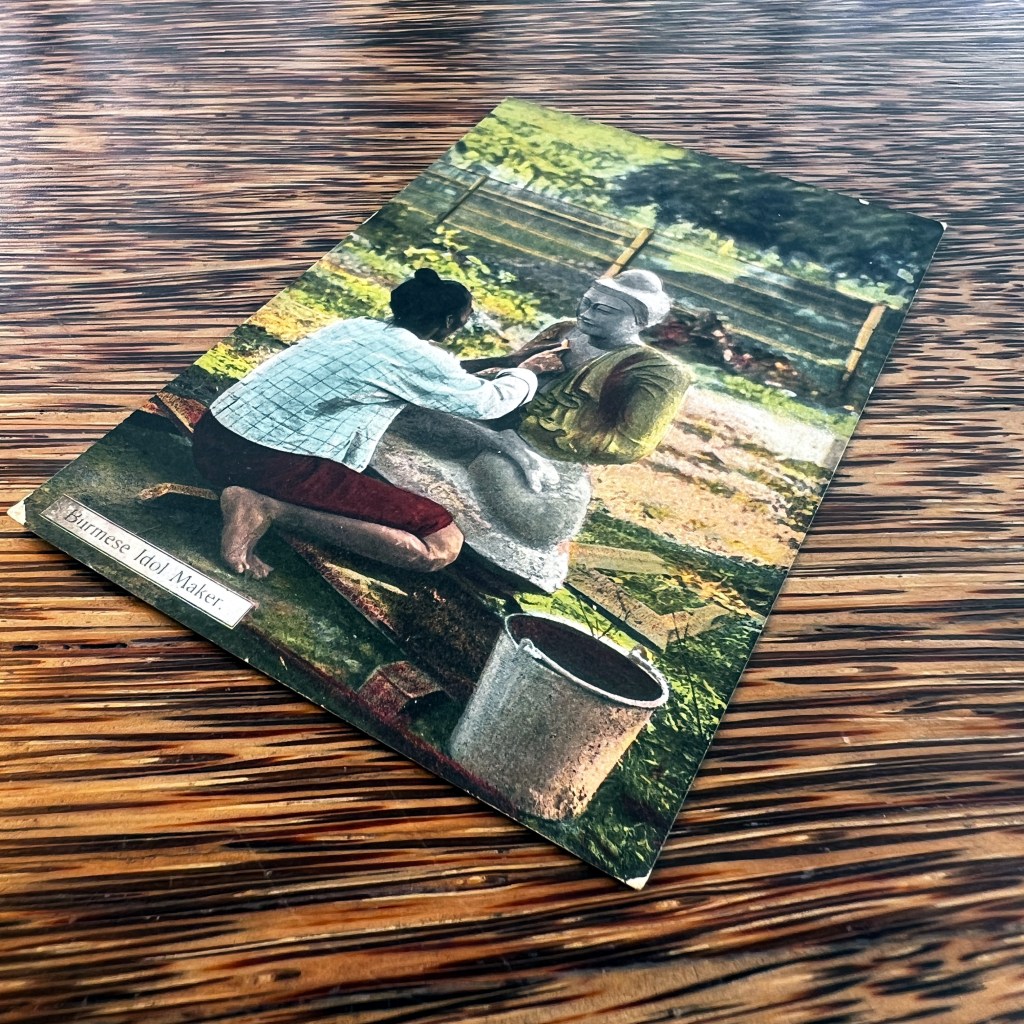
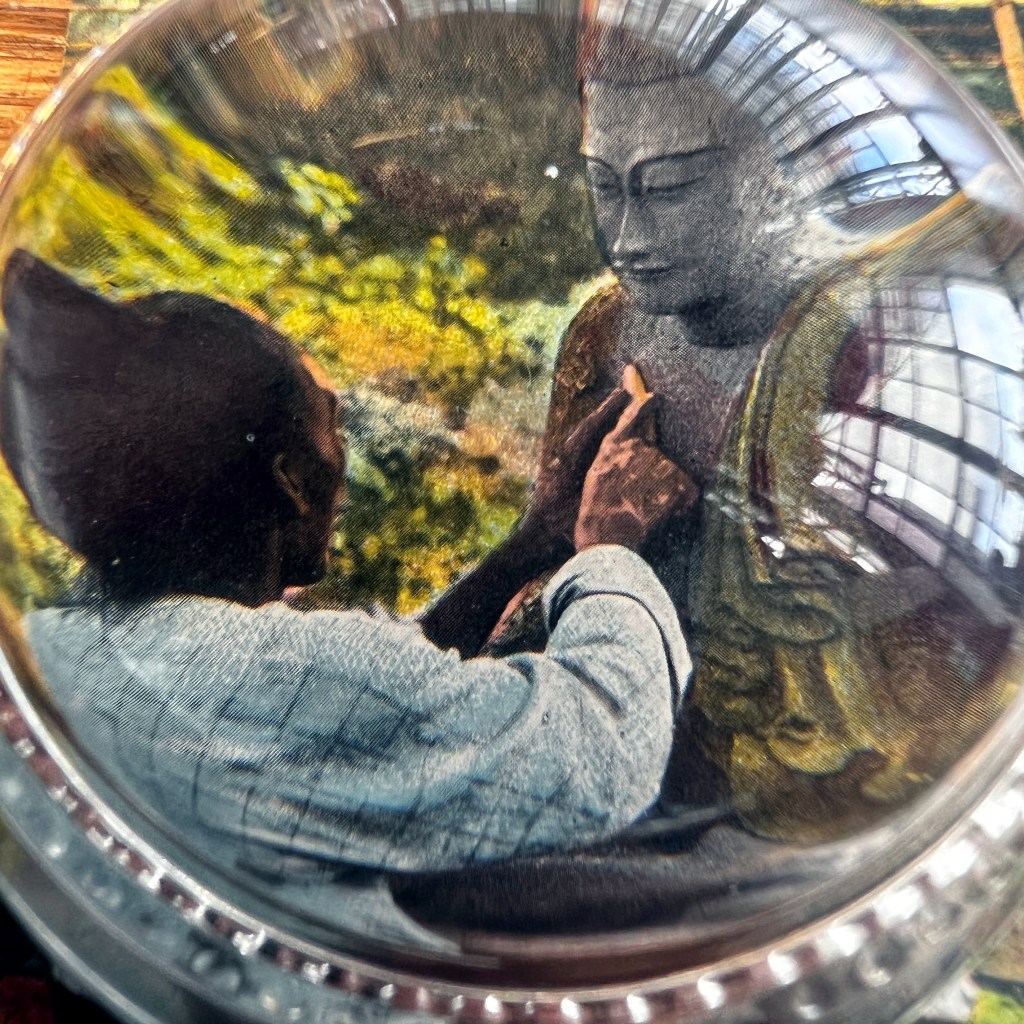
For all the new Buddhas in the West posts
follow us on Bluesky & Instagram
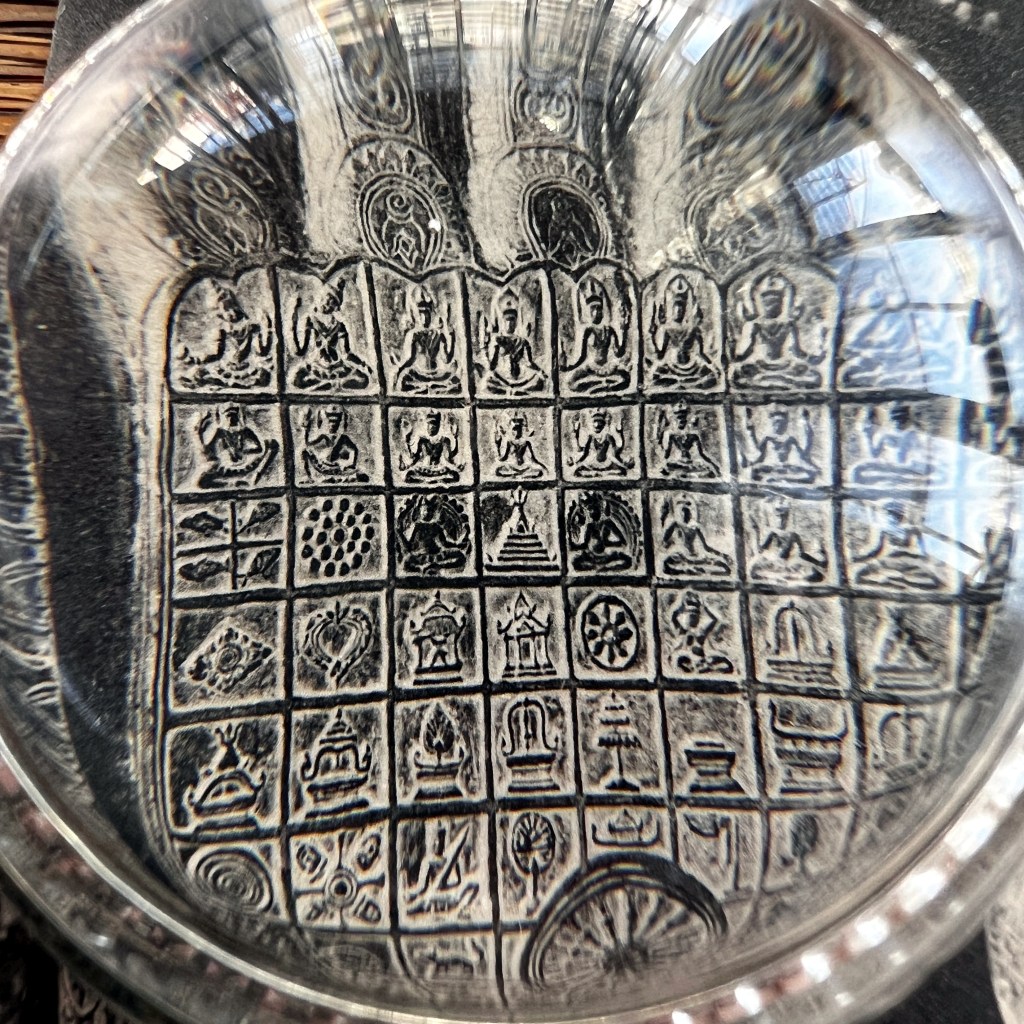
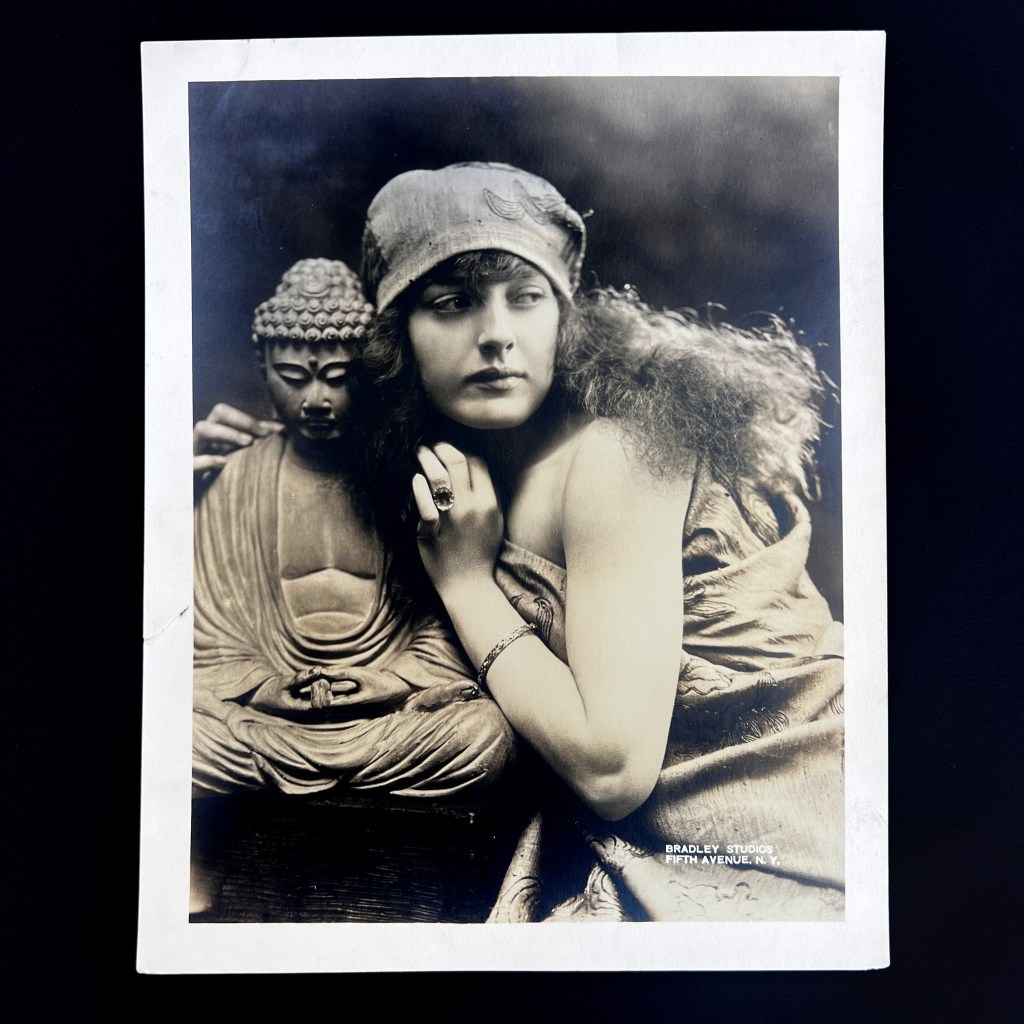
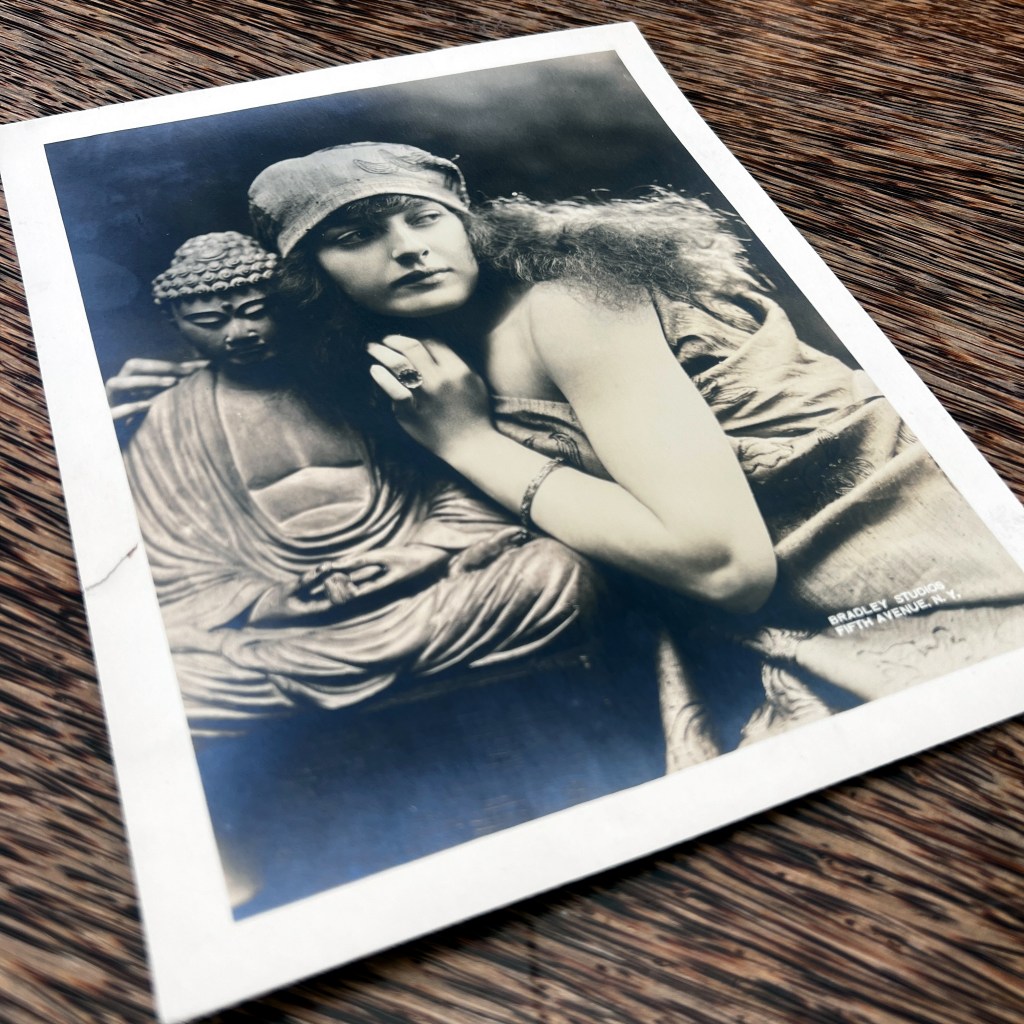
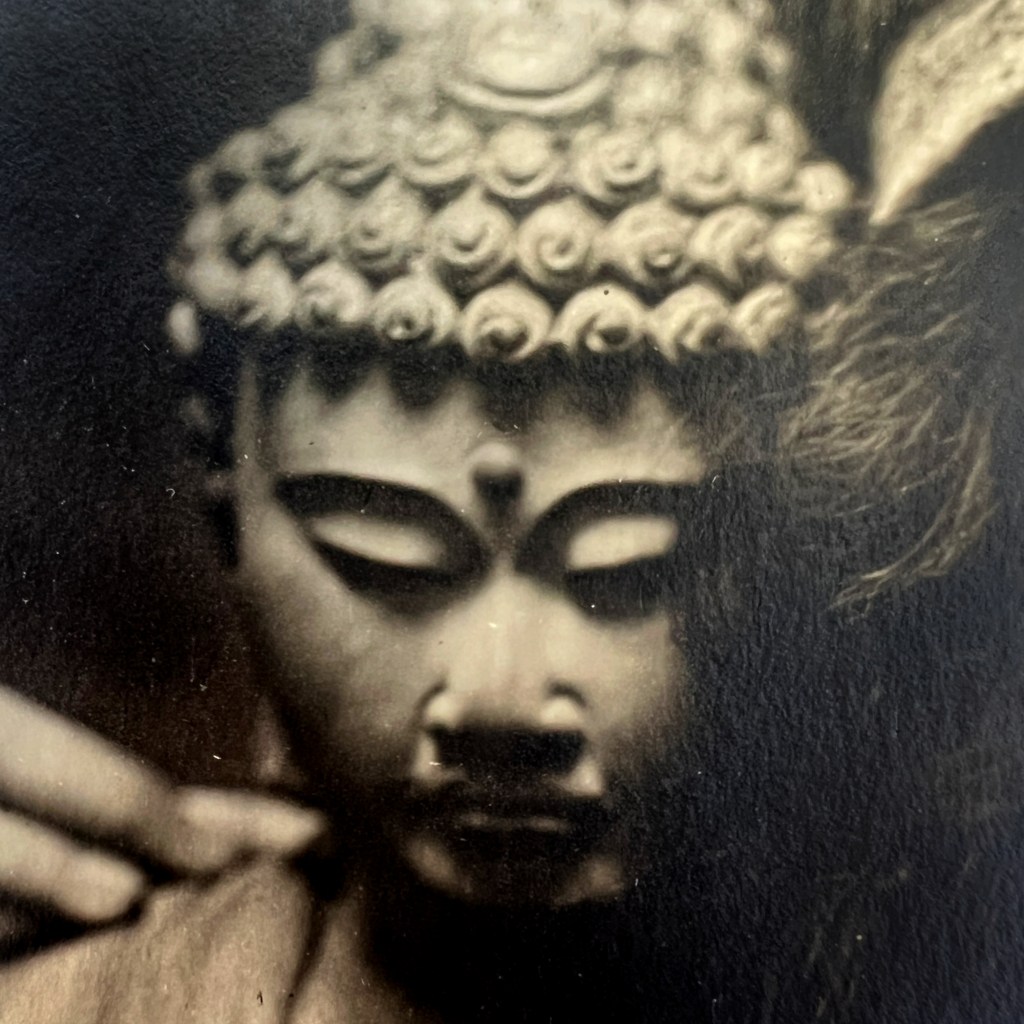
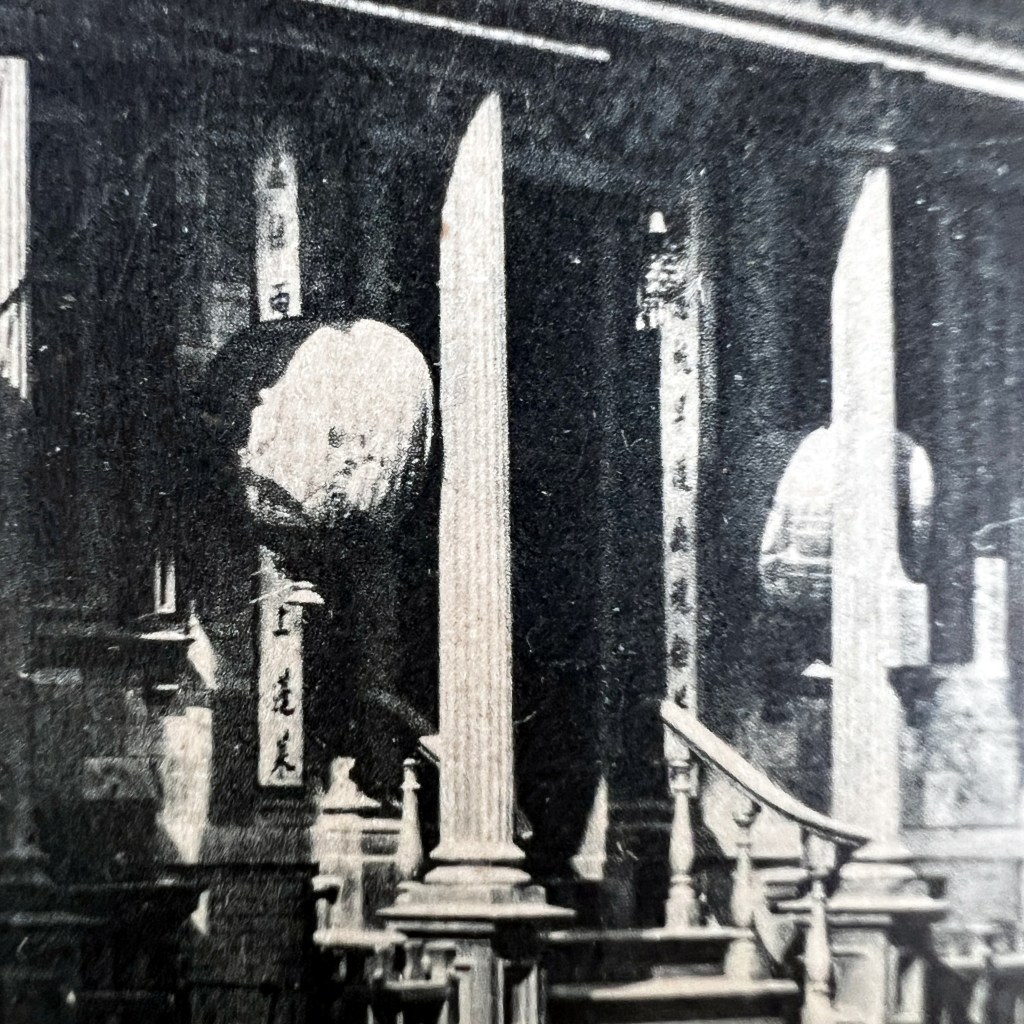
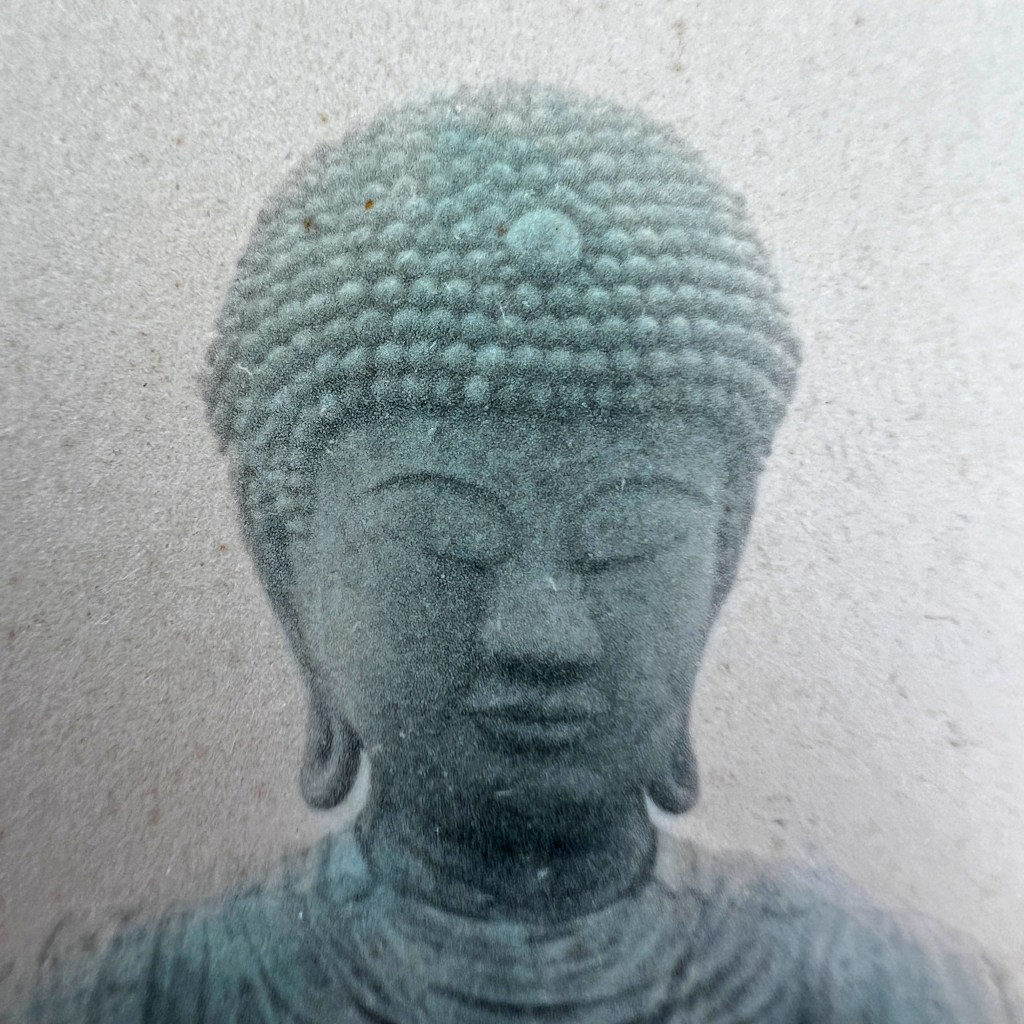
The original Hyōgo Daibutsu at Nōfuku-ji was the third largest Buddhist statue in Japan. It was dismantled by the Ordinance on the Collection of Metals issued in 1941 as part of Japanese war efforts during WWII.

Located in the port city of Kobe, the Daibutsu was approximately 12 meters in height. It became a popular tourist destination at the end of the 19th century, thus many photographs and postcards remain of the now lost icon.
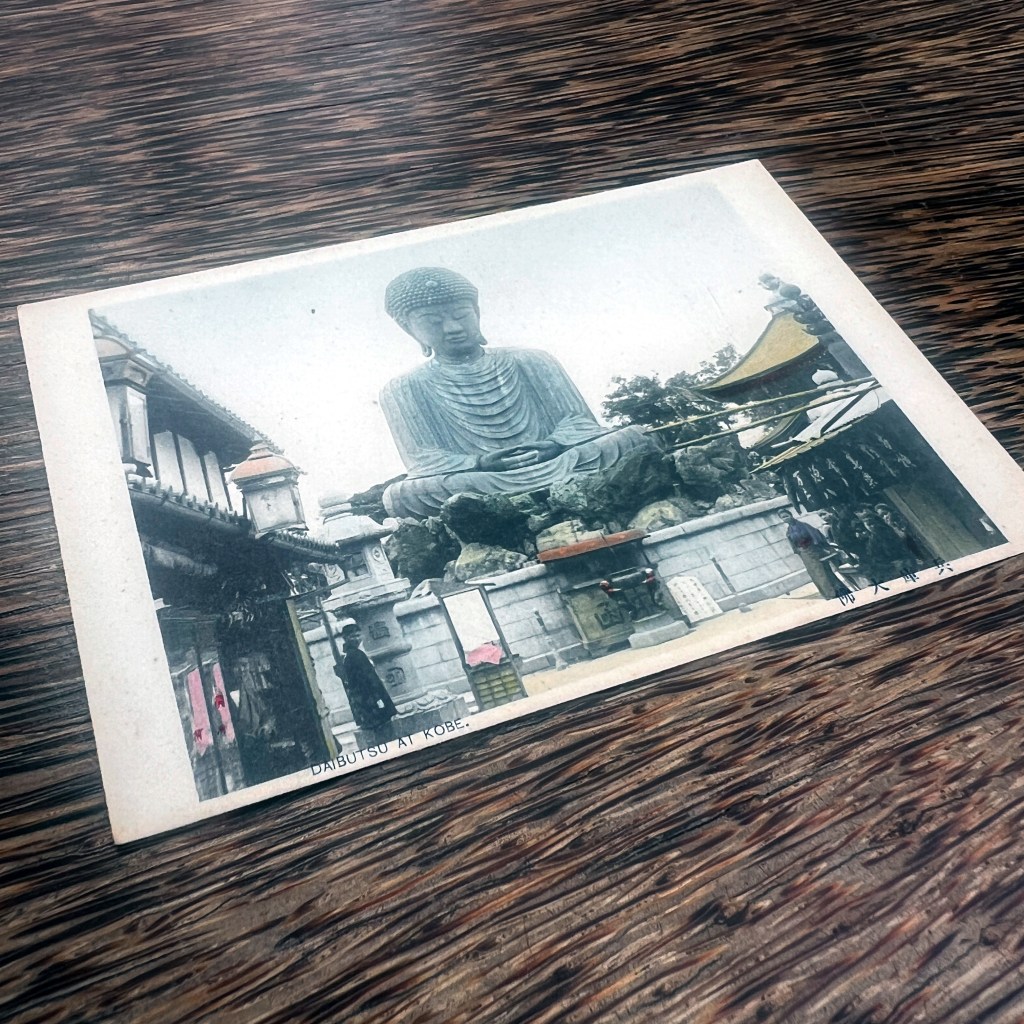

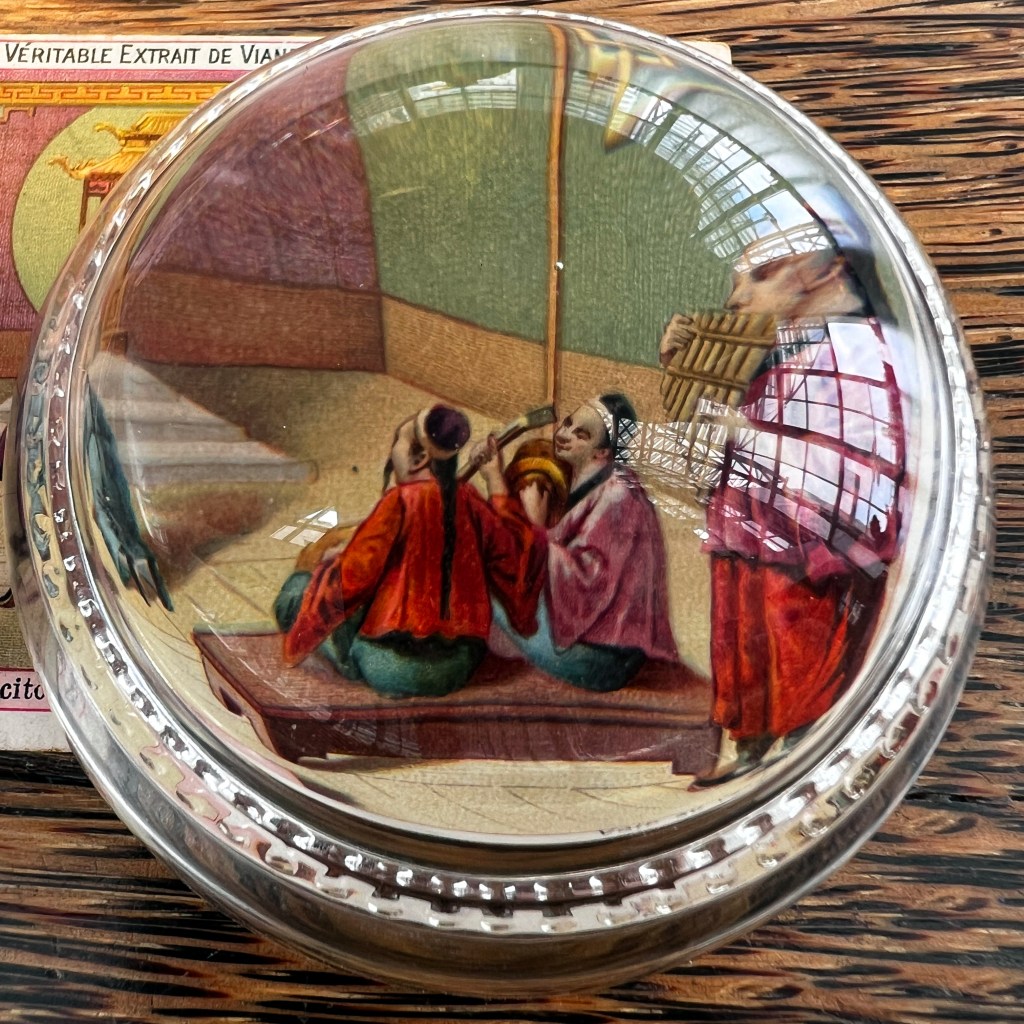
This “undivided back” design informs us the postcard was printed before 1907. The “F.S.” in the stamp box refers to the publisher’s name (which I haven’t identified).

Many Japanese postcards of this period were hand-colored collotype prints. You can see the red ink splotches the colorist used to suggest design elements.

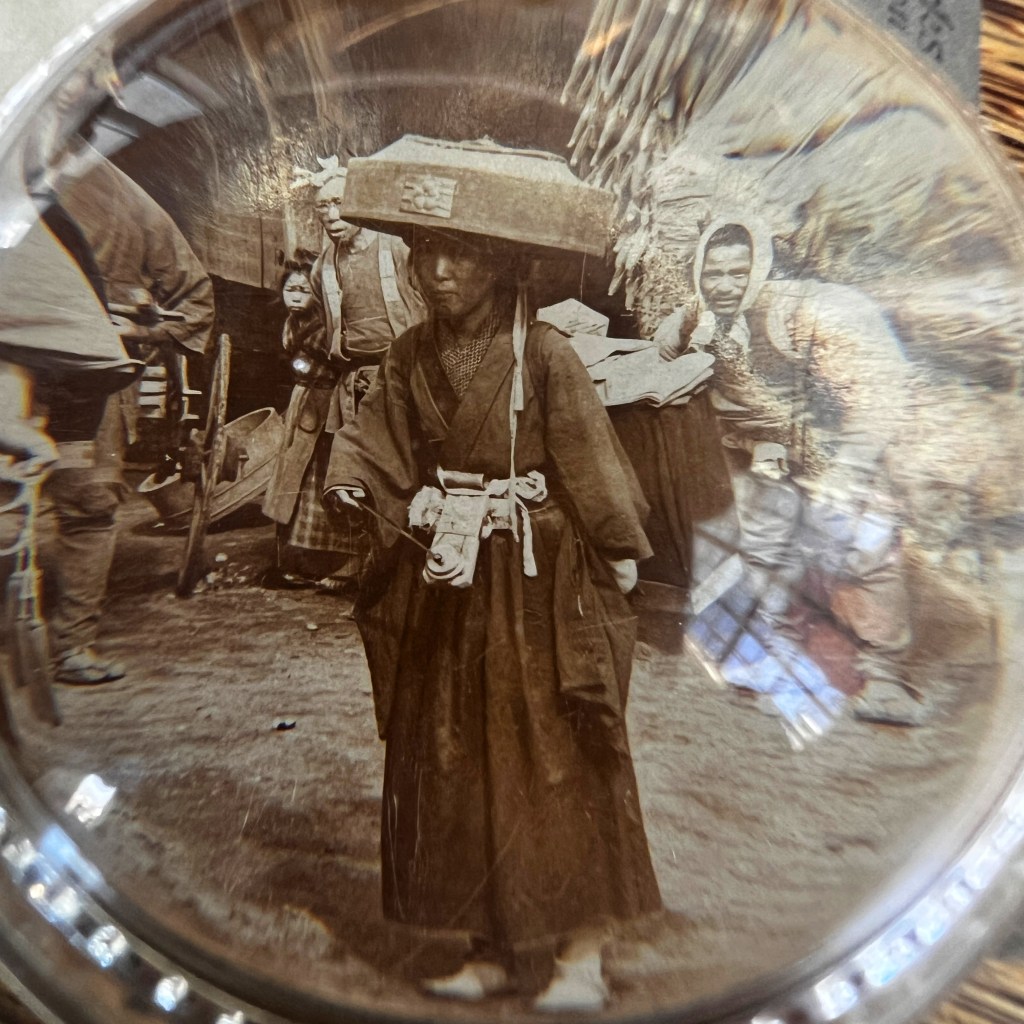
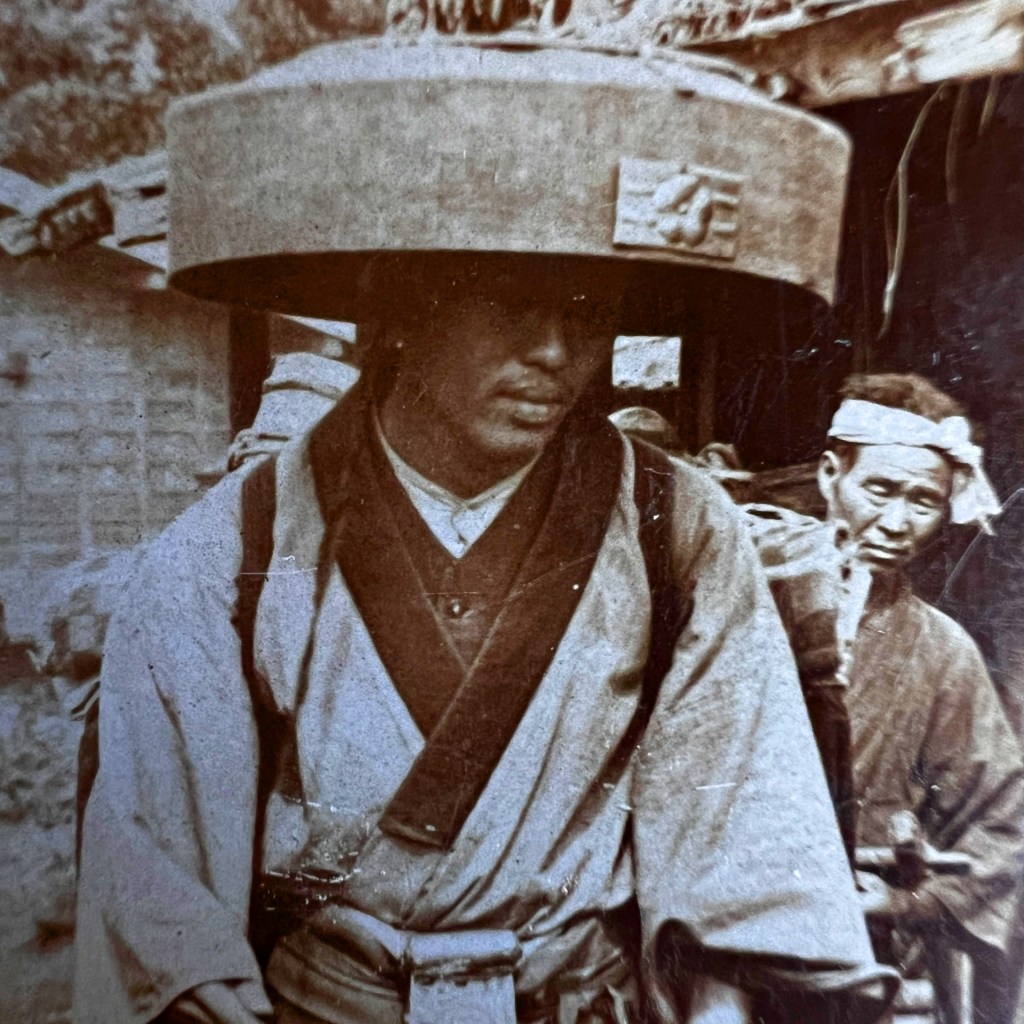
An albumen print photograph by Kusakabe Kinbei is held by the Nagasaki University Library, viewable here: http://oldphoto.lb.nagasaki-u.ac.jp/zoom/jp/record.php?id=1044


The Buddhas in the West Material Archive is a digital scholarship project that catalogues artifacts depicting Buddhist material culture for Western audiences. It’s comprised of prints, photos, and an assortment of ephemera and other objects. For a brief introduction to this archive, visit the main Buddhas in the West project page.
For Related Buddhas in the West Posts Featuring Postcards:
For the Most Recent Buddhas in the West Posts: