For all the new Buddhas in the West posts
follow us on Bluesky & Instagram
At the end of the 19th century, glass “magic lantern” slides were part of popular American entertainment. After returning home, world travelers sometimes gave informal lectures in church halls or town theaters about their experiences, often using these slides.

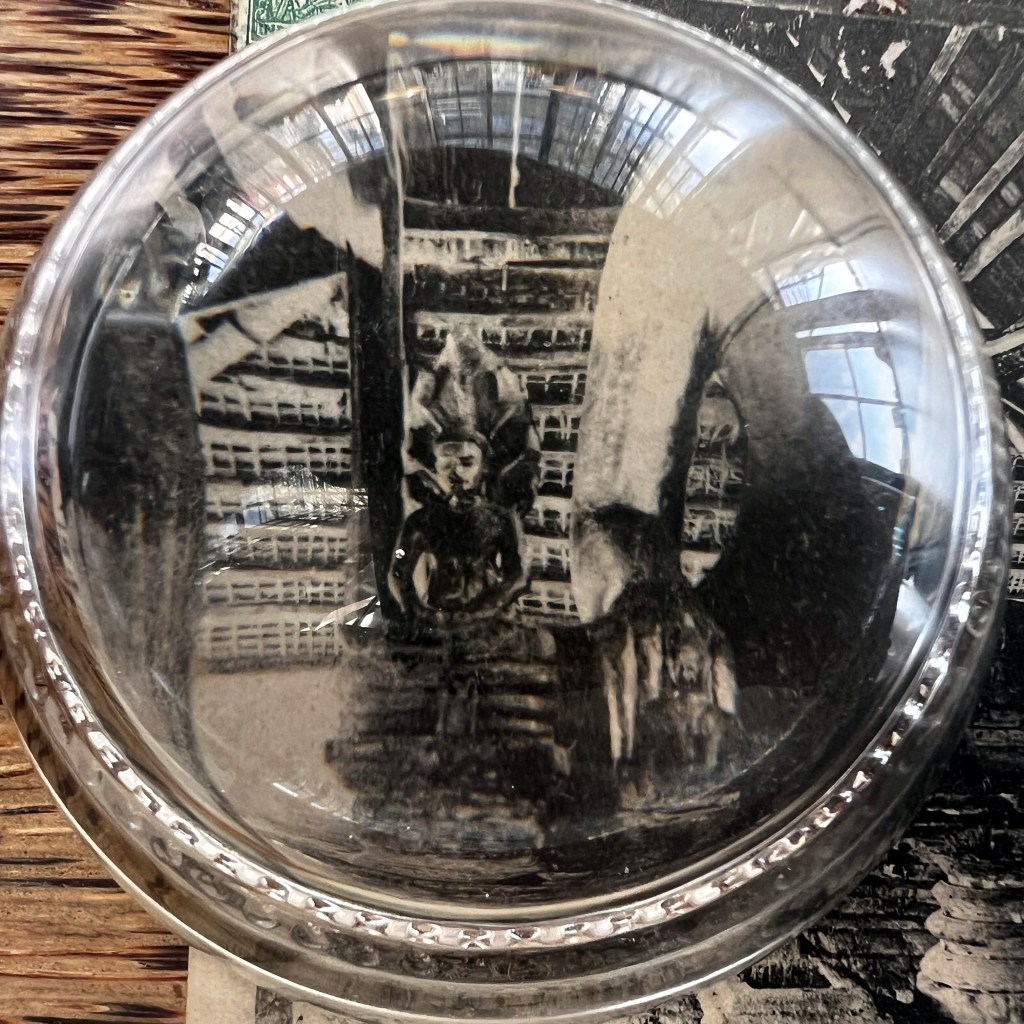
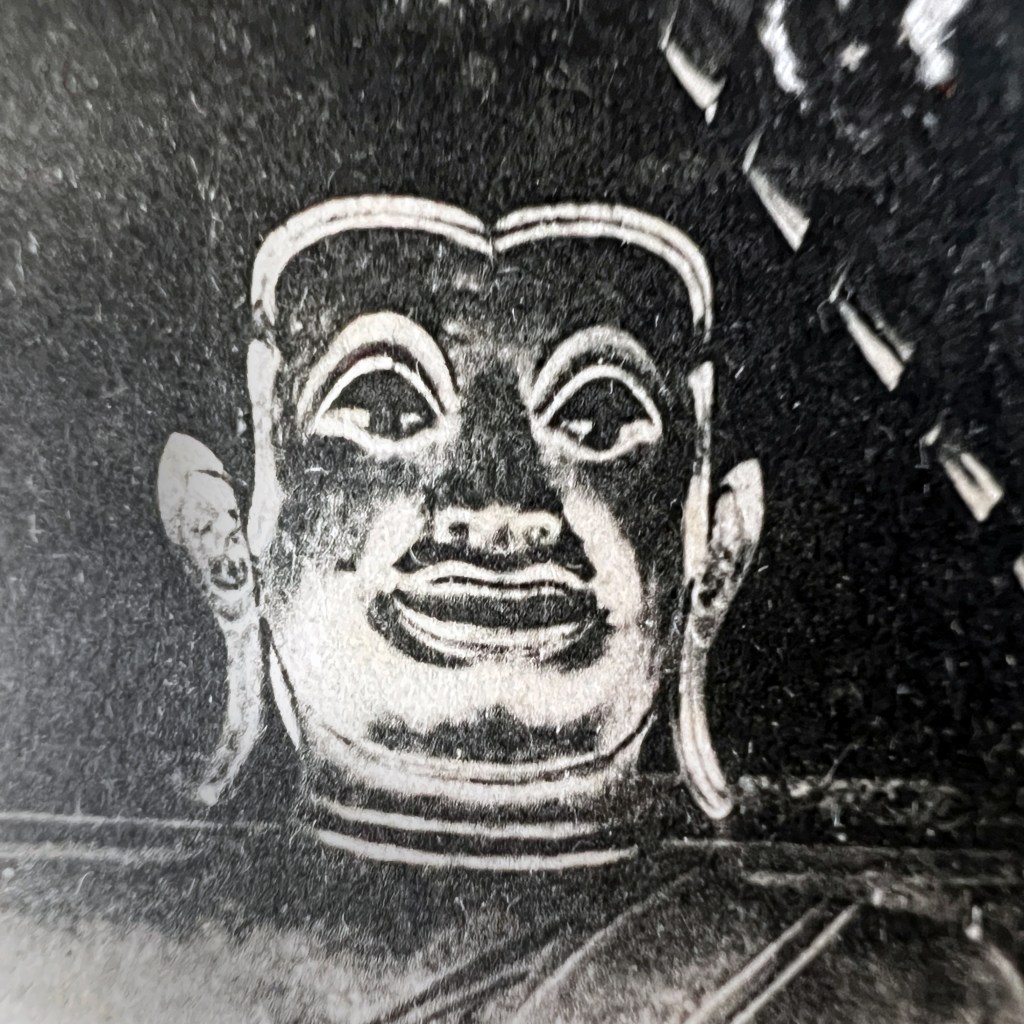
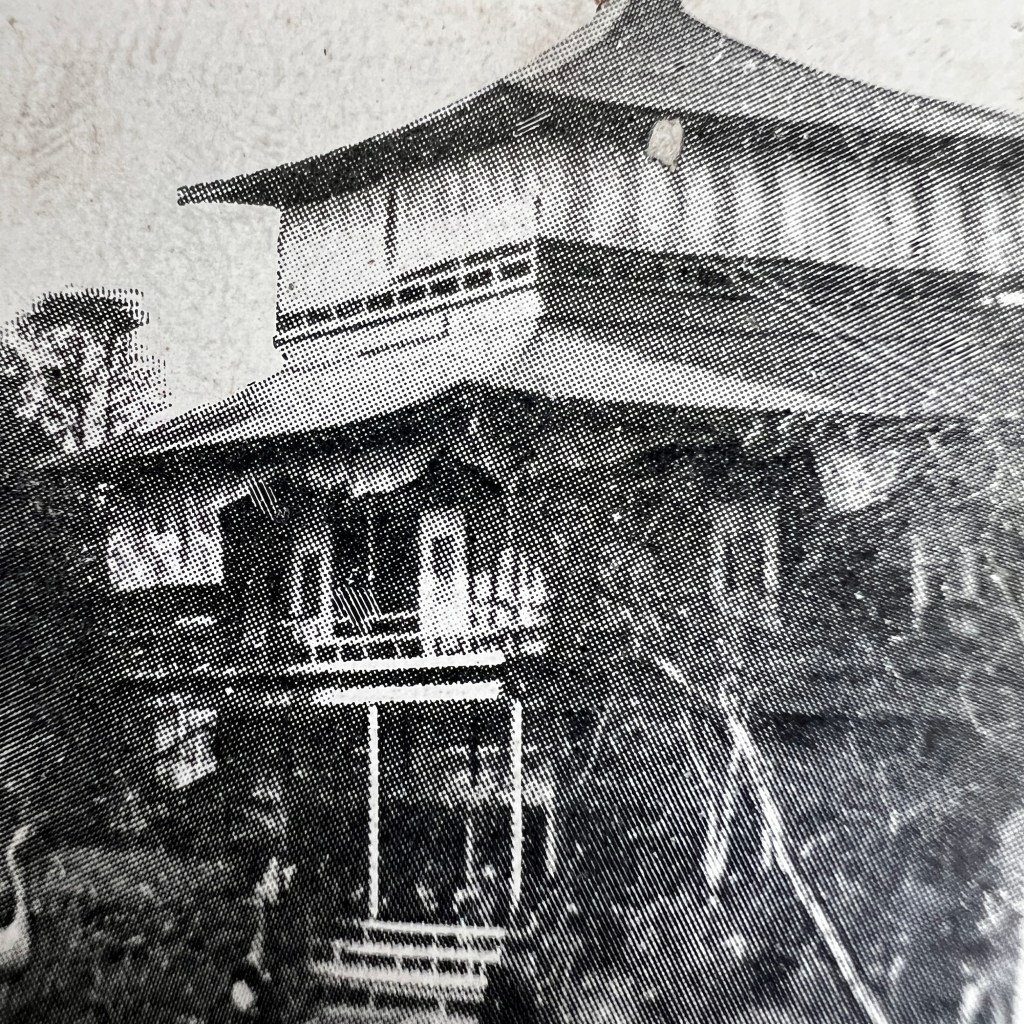
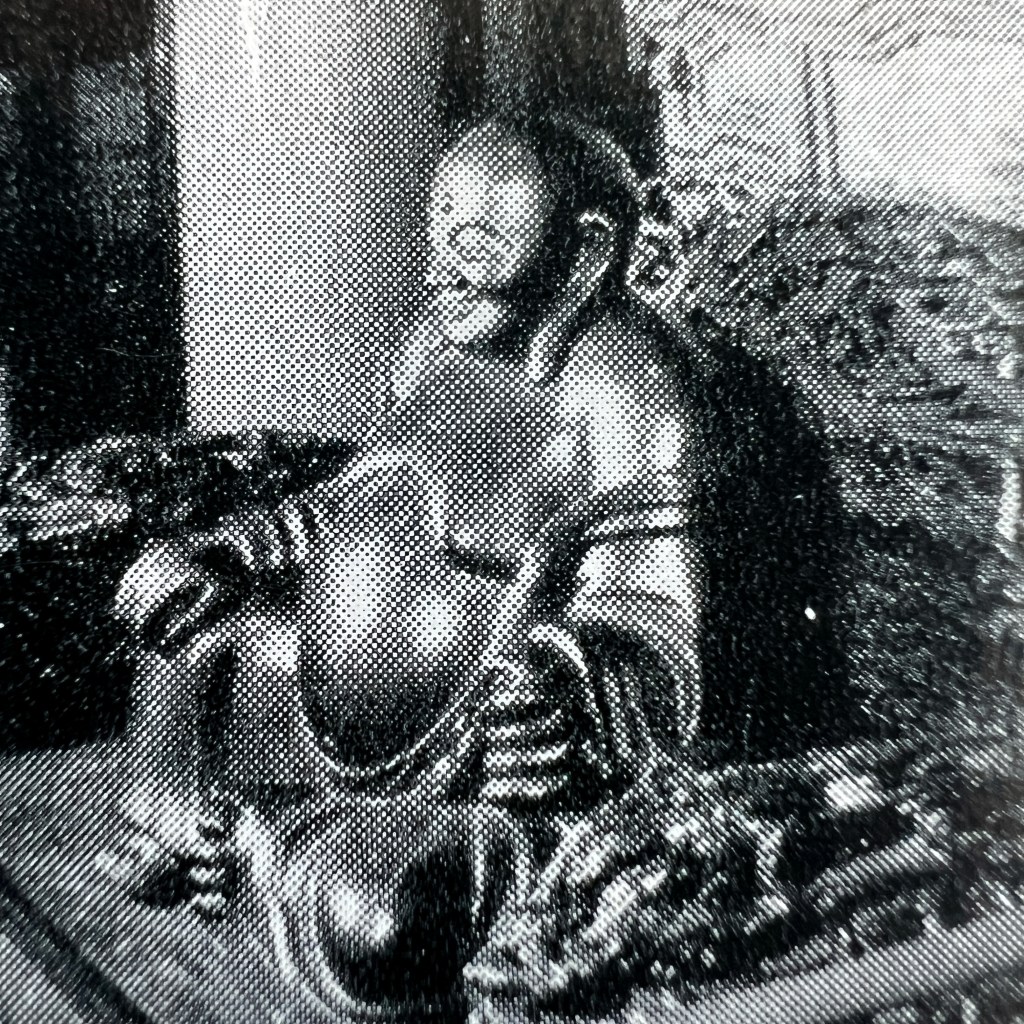
This monumental Jizō was created c. 1300 and sits by a mountain pass where travelers on the famed Tōkaidō made their journey. We can see the rocky outlines of an old wooden roof; the small shrine hall was destroyed during an eruption of Mt. Fuji in 1707.

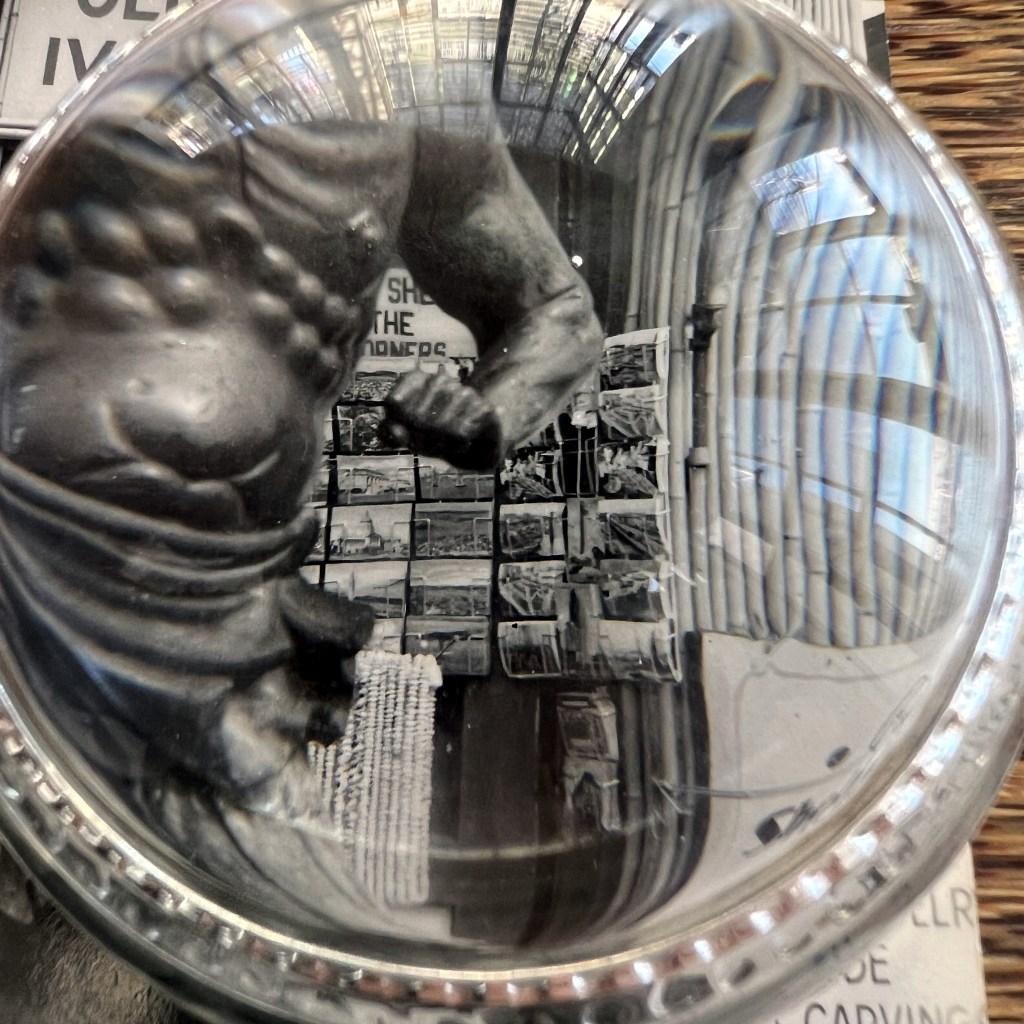
The slide was produced by a New York studio and featured an unknown Euro-American tourist center frame.

Japanese porters can be seen among the entourage.

The photosensitive emulsion is sandwiched between two panels of glass for protection. The tape around the edges holds the glass panels together.

The Hakone Pass Jizō was a popular tourist destination at the turn of the 20th century; it is still viewable today. For more on Jizō and this particular icon, see Hank Glassman, The Face of Jizo: Image and Cult in Medieval Japanese Buddhism, 2012.


The Buddhas in the West Material Archive is a digital scholarship project that catalogues artifacts depicting Buddhist material culture for Western audiences. It’s comprised of prints, photos, and an assortment of ephemera and other objects. For a brief introduction to this archive, visit the main Buddhas in the West project page.
For Related Buddhas in the West Posts Featuring Lantern Slides:
For the Most Recent Buddhas in the West Posts: